IL-6 and CD4+/CD8+ are Important Indicators for Predicting Prognosis in Elderly AECOPD Patients: A Retrospective Study
- PMID: 40008081
- PMCID: PMC11853116
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S496735
IL-6 and CD4+/CD8+ are Important Indicators for Predicting Prognosis in Elderly AECOPD Patients: A Retrospective Study
Abstract
Purpose: Evaluating the role of IL-6 and CD4+/CD8+ in predicting the prognosis of elderly patients with acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (AECOPD).
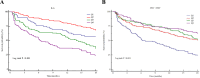
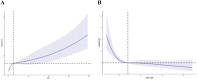
Patients and methods: This study retrospectively enrolled 413 elderly patients who were hospitalized for AECOPD between January 2019 and December 2021. Patients were divided into event and non-event groups based on whether they were readmitted or died due to AECOPD during 18 months of follow-up. The associations between IL-6 and CD4+/CD8+ with adverse events were assessed using Cox proportional hazards regression models, Kaplan-Meier survival analysis, and restricted cubic spline (RCS) models. Additionally, subgroup analyses were conducted to evaluate the stability of these associations, and ROC curves were used to assess the predictive ability of IL-6 combined with CD4+/CD8+ for adverse events.
Results: A total of 413 patients were included in the study, with 218 experiencing adverse events. Patients with high levels of IL-6 and low levels of CD4+/CD8+ had a higher risk of adverse events. There was a non-linear relationship between IL-6 and CD4+/CD8+ with adverse events (p<0.05). Subgroup analyses further confirmed the robustness of this association. ROC curve analysis indicated that combining IL-6 with CD4+/CD8+ significantly improved the predictive value for adverse events.
Conclusion: There is a non-linear relationship between IL-6 and CD4+/CD8+ and adverse events in elderly patients with AECOPD. Combining IL-6 with CD4+/CD8+ ratios significantly enhances the predictive value for adverse events.
Keywords: CD4+/CD8+; IL-6; acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; elderly; prognosis.
© 2025 Liu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest related to this study.
Figures




References
-
- Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (2019 Report). Global initiative for chronic obstructive lung disease.
-
- Wang X, Jiang Y. Disease burden of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in the BRICS countries from 1990 to 2019. Chin Gen Pract. 2024;27(09):1118–1125.
-
- Pantzaris ND, Spilioti DX, Psaromyalou A, Koniari I, Velissaris D. The use of serum procalcitonin as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbations: a literature review update. J Clin Med Res. 2018;10(7):545–551. doi:10.14740/jocmr3458w - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

