RND1 Induces Ferroptosis to Alleviate Inflammatory Response, Proliferation, Invasion, and Migration of Rheumatoid Synoviocytes
- PMID: 40008082
- PMCID: PMC11853921
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S500630
RND1 Induces Ferroptosis to Alleviate Inflammatory Response, Proliferation, Invasion, and Migration of Rheumatoid Synoviocytes
Abstract
Background: Ferroptosis is involved in the occurrence and development of inflammatory arthritis. RND1 has been reported to possess pro-ferroptosis activity.
Objective: This study was designed to explore the role and the molecular mechanism of RND1 in rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
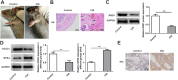
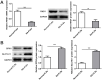
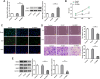
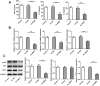
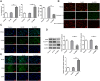
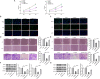
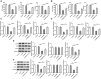
Methods: DBA/1 mice were exposed to type II collagen immunization. The pathological damage of the knee joints of mice was observed with H&E staining and RND1 expression in synovial tissues was detected using Western blot. In vitro, Western blot was used to measure RND1, ferroptosis-, migration- and inflammation-related proteins. The cell proliferation, migration and invasion were detected using CCK-8 method, EdU staining, wound healing and transwell assays. The levels of inflammatory factors were detected with ELISA and RT-qPCR. Relative iron level, GSH and MDA concentrations were detected with corresponding assay kits. BODIPY 581/591 C11 kit measured lipid ROS. 4-HNE and GPX4 expression were detected using immunofluorescence assay.
Results: This study found that RND1 expression was reduced in the synovial tissues of RA mice and human fibroblast-like MH7A synoviocytes. It was also found that the upregulation of RND1 inhibited the proliferation, migration, invasion and inflammatory response in rheumatoid synovial cells via ferroptosis.
Conclusion: Collectively, RND1 exerted protective impacts on RA, which might be mediated by ferroptosis.
Keywords: RND1; ferroptosis; fibroblast-like synoviocytes; rheumatoid arthritis.
© 2025 Chen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Amentoflavone Induces Ferroptosis to Alleviate Proliferation, Migration, Invasion and Inflammation in Rheumatoid Arthritis Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes by Inhibiting PIN1.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025 Mar;83(1):1299-1312. doi: 10.1007/s12013-024-01563-8. Epub 2024 Oct 1. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025. PMID: 39354278
-
The therapeutic effect of wasp venom (Vespa magnifica, Smith) and its effective part on rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes through modulating inflammation, redox homeostasis and ferroptosis.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Dec 5;317:116700. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116700. Epub 2023 Jun 12. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37315652
-
Therapeutic effects of shikonin on adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats and cellular inflammation, migration and invasion of rheumatoid fibroblast-like synoviocytes via blocking the activation of Wnt/β-catenin pathway.Phytomedicine. 2023 Jul 25;116:154857. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154857. Epub 2023 May 3. Phytomedicine. 2023. PMID: 37163904
-
A novel function of artesunate on inhibiting migration and invasion of fibroblast-like synoviocytes from rheumatoid arthritis patients.Arthritis Res Ther. 2019 Jun 24;21(1):153. doi: 10.1186/s13075-019-1935-6. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 31234900 Free PMC article.
-
Schisandrin treatment suppresses the proliferation, migration, invasion, and inflammatory responses of fibroblast-like synoviocytes from rheumatoid arthritis patients and attenuates synovial inflammation and joint destruction in CIA mice.Int Immunopharmacol. 2023 Sep;122:110502. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110502. Epub 2023 Jun 28. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37390648
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

