Effects of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists, Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors, and Their Combination on Neurohumoral and Mitochondrial Activation in Patients With Diabetes
- PMID: 40008510
- PMCID: PMC12132653
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.124.039129
Effects of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists, Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors, and Their Combination on Neurohumoral and Mitochondrial Activation in Patients With Diabetes
Abstract
Background: We investigated the effects of the combined treatment with glucagon like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RA) and sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors (SGLT-2i) on NT-proBNP (N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide), GDF-15 (growth differentiation factor 15), and MOTS-c (mitochondrial-derived peptide-c) in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) and high or very high cardiovascular risk.
Methods: We studied 163 consecutive patients with type 2 diabetes who were treated with insulin (n=40), liraglutide (n=41), empagliflozin (n=42), or their combination (GLP-1RA+SGLT-2i) (n=40) and were matched using propensity score analysis. We measured the following at baseline and 4 and 12 months of treatment: (1) NT-proBNP, GDF-15, and MOTS-c; (2) 2,2'-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid), and (3) left ventricular global longitudinal strain, left atrial strain during atrial reservoir phase, and global work index using speckle-tracking imaging.
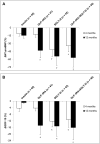
Results: At 12 months, GLP-1RA, SGLT-2i, and their combination showed a greater reduction of NT-proBNP (-43.1% versus -54.2% versus -56.9% versus -14.7%) and GDF-15 than insulin. Only treatment with SGLT-2i and GLP-1RA+SGLT-2i improved MOTS-c. GLP-1RA, SGLT-2i, or GLP-1RA+SGLT-2i provided an increase of global longitudinal strain, left atrial strain, and global work index compared with insulin. In all patients, the reduction of NT-proBNP was associated with the improvement of global longitudinal strain, left atrial strain during atrial reservoir phase, and global work index; the decrease of GDF-15 with the increase of ABTS and MOTS-c; and the increase of MOTs-c with improved global longitudinal strain and constructive myocardial work at 12 months (P<0.05).
Conclusions: Twelve-month treatment with combination of GLP-1RA+SGLT-2i was associated with a greater reduction of neurohumoral markers and increase of antioxidant ability than each treatment alone and insulin. SGLT-2i appear more effective in the improvement of neurohumoral and mitochondrial activation.
Registration: URL: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov; Unique identifier: NCT03878706.
Keywords: N‐terminal pro‐brain natriuretic peptide; glucagon like peptide‐1 receptor agonists; growth differentiation factor 15; mitochondrial‐derived peptide‐c; sodium‐glucose cotransporter‐2 inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


References
-
- Seferović PM, Petrie MC, Filippatos GS, Anker SD, Rosano G, Bauersachs J, Paulus WJ, Komajda M, Cosentino F, de Boer RA, et al. Type 2 diabetes mellitus and heart failure: a position statement from the heart failure Association of the European Society of cardiology. Eur J Heart Fail. 2018;20:853–872. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.1170 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sharma A, Vaduganathan M, Ferreira JP, Liu Y, Bakris GL, Cannon CP, White WB, Zannad F. Clinical and biomarker predictors of expanded heart failure outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus after a recent acute coronary syndrome: insights from the EXAMINE trial. J Am Heart Assoc. 2020;9:e012797. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.119.012797 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

