Reflecting on Fleming's caveat: the impact of stakeholder decision-making on antimicrobial resistance evolution
- PMID: 40008972
- PMCID: PMC11865498
- DOI: 10.1099/mic.0.001534
Reflecting on Fleming's caveat: the impact of stakeholder decision-making on antimicrobial resistance evolution
Abstract
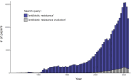
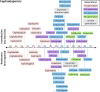
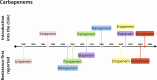
Antimicrobial resistance poses one of the greatest and most imminent threats to global health, environment and food security, for which an urgent response is mandated. Evolutionary approaches to tackling the crisis tend to focus on proximate issues including the mechanisms and pathways to resistance, with associated calls to action for infection control and antimicrobial stewardship. This is of clear benefit but overlooks the fundamental influence of policy and stakeholder decision-making on resistance evolution. In 1945, Fleming issued a stark warning on the irresponsible use of penicillin and its potential to cause death due to penicillin-resistant infections. Attention to resistance evolution theory and heeding Fleming's advice could have allowed for a vastly different reality. Embedding evolutionary theory within policy, industry and regulatory bodies is not only essential but is now a race against time. Hence, critical appraisal of historical behaviour and attitudes at a global scale can inform a paradigm of anticipatory and adaptive policy. To undertake this exercise, we focused on the largest group of antibiotics with the greatest clinical and economic footprint, the beta-lactams. We examined historical case studies that affected how beta-lactams were developed, produced, approved and utilized, in order to relate stakeholder decision-making to resistance evolution. We derive lessons from these observations and propose sustainable approaches to curb resistance evolution. We set a position that actively incorporates an evolutionary theory of antimicrobial resistance into decision-making within antimicrobial development, production and stewardship.
Keywords: antimicrobial resistance; global response to antimicrobial resistance (AMR); policy; stewardship.
Conflict of interest statement
T.A. was an employee of Pfizer Ltd at project initiation. T.A. is an elected trustee of the British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy and the director of thesignpost.com and has recent consultancy contracts with ESSITY, Menarini, Pharmafilter, ADVANZ, BinaryPharma and UK Sepsis Trust. Z.R. is an employee and shareholder of Pfizer Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- UN Environment Programme Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) 2024. https://www.unep.org/topics/chemicals-and-pollution-action/pollution- an...
-
- O’Neill J. Tackling drug resistant infections globally: final report and recommendations. AMR. 2016
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

