CXCL10 Secreted by Pericytes Mediates TNFα-Induced Vascular Leakage in Tumors and Enhances Extravasation of Nanoparticle-Based Chemotherapeutics
- PMID: 40009768
- PMCID: PMC12046328
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-24-3833
CXCL10 Secreted by Pericytes Mediates TNFα-Induced Vascular Leakage in Tumors and Enhances Extravasation of Nanoparticle-Based Chemotherapeutics
Abstract
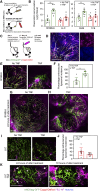
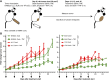
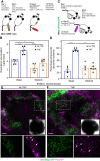
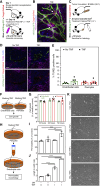
TNFα induces vascular permeability and plays an important role in inflammation. In addition, TNFα-induced vascular leakage is involved in the increased extravasation of nanoparticle-formulated chemotherapeutic drugs, improving drug delivery and subsequent tumor response. In this study, we uncovered a positive correlation between the presence of pericytes in the tumor-associated vasculature and TNFα-induced leakage and drug delivery, especially when drugs were encapsulated in nanoparticles. RNA sequencing and pathway analysis identified high expression of C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 10 (CXCL10) in TNFα-stimulated pericytes. In addition, TNFα increased CXCL10 protein production by pericytes in vitro. In animal studies, tumor types with vessels with high pericyte coverage showed enhanced permeability and extravasation of drugs encapsulated in nanoparticles following treatment with TNFα, which could be blocked with a CXCL10-neutralizing antibody. In contrast, tumors harboring vessels with low pericyte numbers did not display increased drug extravasation in response to TNFα. Lack of pericyte coverage could be compensated by coadministration of CXCL10. These findings reveal a mechanism by which TNFα induces CXCL10 release from pericytes, resulting in increased endothelial permeability, vascular leakage, and drug delivery. Significance: TNFα stimulates tumor-associated pericytes to produce CXCL10 that mediates vascular leakage and assists in the intratumoral delivery of nanoparticle-encapsulated chemotherapeutic drugs.
©2025 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
A.L.B. Seynhaeve reports grants and personal fees from the Dutch Cancer Society and grants and other support from Vereniging Trustfonds Erasmus University Rotterdam and Stichting Erasmus Heelkundig Kankeronderzoek during the conduct of the study. No disclosures were reported by the other authors.
Figures


References
-
- Zelová H, Hošek J. TNF-α signalling and inflammation: interactions between old acquaintances. Inflamm Res 2013;62:641–51. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

