Excess All-Cause Mortality by Age and Gender During the COVID-19 Pandemic in the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bosnia and Herzegovina: 2020-2022
- PMID: 40010310
- PMCID: PMC11864808
- DOI: 10.1111/irv.70086
Excess All-Cause Mortality by Age and Gender During the COVID-19 Pandemic in the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bosnia and Herzegovina: 2020-2022
Abstract
Objectives: COVID-19 has had a profound impact on global mortality and morbidity, yet only a fraction of deaths was confirmed and reported. We estimated all-cause excess mortality from 1 January 2020 to 31 December 2022 in the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina (FBiH) to assess the true magnitude of the pandemic.
Methods: Data for this analysis was sourced from the FBiH mortality register and supplemented with population statistics and official COVID-19 death counts (i.e., cases where COVID-19 was registered as the cause of death). Using a Poisson model, all-cause excess number of deaths and rates per 100,000 person-years, adjusted for registration delays and stratified by age and gender, were calculated.
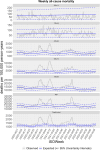
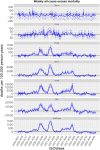
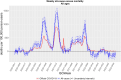
Results: FBiH experienced three periods of excess all-cause mortality throughout the first 3 years of the pandemic, with a total of 12,000 excess deaths, highest among adults 45-74 years and males. No excess mortality was observed in children <15 years.
Conclusions: The true mortality impact of COVID-19 in FBiH was substantially higher than the reported deaths, including among younger adults. Strengthening civil registration and vital statistics, including establishment of all-cause mortality surveillance, is essential for improved monitoring of future pandemics and other important public health events. A detailed review of the direct and indirect effects of COVID-19 on mortality should be conducted to identify areas that require more resources, improve health provision and inform mitigation efforts in future pandemics to save lives.
Keywords: COVID‐19; excess mortality; mortality.
© 2025 The Author(s). Influenza and Other Respiratory Viruses published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Global burden of 288 causes of death and life expectancy decomposition in 204 countries and territories and 811 subnational locations, 1990-2021: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021.Lancet. 2024 May 18;403(10440):2100-2132. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(24)00367-2. Epub 2024 Apr 3. Lancet. 2024. PMID: 38582094 Free PMC article.
-
Global age-sex-specific mortality, life expectancy, and population estimates in 204 countries and territories and 811 subnational locations, 1950-2021, and the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic: a comprehensive demographic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021.Lancet. 2024 May 18;403(10440):1989-2056. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(24)00476-8. Epub 2024 Mar 11. Lancet. 2024. PMID: 38484753 Free PMC article.
-
An assessment of excess mortality during the COVID-19 pandemic, a retrospective post-mortem surveillance in 12 districts - Zambia, 2020-2022.BMC Public Health. 2024 Sep 27;24(1):2625. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-20045-3. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39333953 Free PMC article.
-
Estimating Excess Mortality During the COVID-19 Pandemic Between 2020-2022 in Korea.J Korean Med Sci. 2024 Oct 21;39(40):e267. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2024.39.e267. J Korean Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39435517 Free PMC article.
-
[SENTIERI - Epidemiological Study of Residents in National Priority Contaminated Sites. Sixth Report].Epidemiol Prev. 2023 Jan-Apr;47(1-2 Suppl 1):1-286. doi: 10.19191/EP23.1-2-S1.003. Epidemiol Prev. 2023. PMID: 36825373 Italian.
Cited by
-
The global burden of depression attributable to childhood sexual abuse, intimate partner violence, and bullying victimization from 1990 to 2021: an analysis based on the global burden of disease study.Ann Gen Psychiatry. 2025 Aug 6;24(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s12991-025-00586-6. Ann Gen Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40770343 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO , “Coronavirus (COVID‐19) Dashboard,” accessed: Oct. 27, 2023. [Online], https://covid19.who.int.
-
- “Third Round of the Global Pulse Survey on Continuity of Essential Health Services During the COVID‐19 Pandemic: November–December 2021,” Word Health Organization. [Online], https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/351527/WHO‐2019‐nCoV‐EHS‐con....
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

