APPROACH: Analysis of Proton versus Photon Radiotherapy in Oligodendroglioma and Assessment of Cognitive Health - study protocol paper for a phase III multicentre, open-label randomised controlled trial
- PMID: 40010843
- PMCID: PMC11865786
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-097810
APPROACH: Analysis of Proton versus Photon Radiotherapy in Oligodendroglioma and Assessment of Cognitive Health - study protocol paper for a phase III multicentre, open-label randomised controlled trial
Abstract
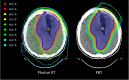
Introduction: Oligodendroglioma (ODG) is a rare type of brain tumour, typically diagnosed in younger adults and associated with prolonged survival following treatment. The current standard of care is maximal safe debulking surgery, radiotherapy (RT) and adjuvant procarbazine, lomustine and vincristine (PCV) chemotherapy. Patients may experience long-term treatment-related toxicities, with RT linked to impairments of neurocognitive function (NCF) and health-related quality of life (HRQoL). With proton beam therapy (PBT), radiation dose falls off sharply beyond the target with reduced normal brain tissue radiation doses compared with photon RT. Therefore, PBT might result in reduced radiation-induced toxicity compared with photon RT.
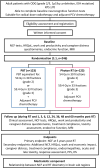
Methods and analysis: APPROACH is a multicentre open-label phase III randomised controlled trial of PBT versus photon RT in patients with ODG, investigating the impact of PBT on long-term NCF measured using the European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) Core Clinical Trial Battery Composite (CTB COMP). The trial will randomise 246 participants from 18 to 25 UK RT sites, allocated 1:1 to receive PBT or photon RT, with PBT delivered at one of the two UK PBT centres. Participants with grade 2 and grade 3 ODG will receive 54 Gy in 30 fractions and 59.4 Gy in 33 fractions, respectively, followed by 6×6-weekly cycles of PCV chemotherapy. The trial contains staged analyses, with an internal pilot for feasibility of recruitment at 12 months, early assessment of efficacy at 2 years, futility assessment and final primary endpoint comparison of NCF between arms at 5 years. Secondary endpoints include additional NCF, treatment compliance, acute and late toxicities, endocrinopathies, HRQoL, tumour response, progression-free survival and overall survival.
Ethics and dissemination: Ethical approval was obtained from Newcastle North Tyneside REC (reference 22/NE/0232). Final trial results will be published in peer-reviewed journals and adhere to International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) guidelines.
Trial registration number: ISRCTN:13390479.
Keywords: Neurological oncology; RADIOTHERAPY; Randomized Controlled Trial.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: FS is supported by a Cancer Research UK Clinical Trial Fellowship (award number 125713). LM is an associate professor funded by Yorkshire Cancer Research (award number L389LM). FWB is an associate professor funded by Yorkshire Cancer Research (award number L389FB). All other authors have no competing interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Cancer Research UK Oligodendroglioma. 2019. https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/about-cancer/brain-tumours/types/oligod... Available.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
