Thrombin cleaves membrane-bound endoglin potentially contributing to the heterogeneity of circulating endoglin in preeclampsia
- PMID: 40011679
- PMCID: PMC11865430
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-025-07751-3
Thrombin cleaves membrane-bound endoglin potentially contributing to the heterogeneity of circulating endoglin in preeclampsia
Abstract
Increased levels of soluble endoglin (sEng) are found in serum, plasma, and urine of preeclampsia patients. sEng is released from membrane-bound endoglin through the proteolytic activity of metalloproteases, but its structural heterogeneity suggests the involvement of additional proteases. Considering the roles of thrombin and sEng in preeclampsia pathogenesis, we investigated whether thrombin cleaves endoglin. Sequence analysis revealed a conserved peptide in endoglin similar to the α-thrombin cleavage site of protease-activated receptor-1. Western blot analysis of plasma from preeclamptic women showed endoglin fragments consistent with thrombin-mediated cleavage. Incubation of purified endoglin with thrombin generated specific fragments, whose N- and C-terminal sequencing confirmed the predicted cleavage sites. Furthermore, thrombin treatment of endoglin-expressing cells released sEng and reduced cell surface endoglin. These findings suggest that multiple protease-targeted cleavage sites lead to the generation of sEng fragments, which may reflect endothelial dysfunction and preeclampsia progression.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: A patent (No. EP24307100) entitled ‘Peptide derived from endoglin for treating bleeding disorders’ was filed by inventor Elisa Rossi and supported by INSERM Transfert (Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale) in France.
Figures
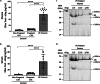

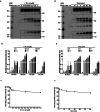


References
-
- López-Novoa, J. M. & Bernabeu, C. The physiological role of endoglin in the cardiovascular system. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol.299, H959–H974 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Rossi, E. et al. Co-injection of mesenchymal stem cells with endothelial progenitor cells accelerates muscle recovery in hind limb ischemia through an endoglin-dependent mechanism. Thromb. Haemost.117, 1908–1918 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Shovlin, C. L. Hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia: Pathophysiology, diagnosis and treatment. Blood Rev.24, 203–219 (2010). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

