Establishment of a predictive nomogram for breast cancer lympho-vascular invasion based on radiomics obtained from digital breast tomography and clinical imaging features
- PMID: 40011817
- PMCID: PMC11866887
- DOI: 10.1186/s12880-025-01607-2
Establishment of a predictive nomogram for breast cancer lympho-vascular invasion based on radiomics obtained from digital breast tomography and clinical imaging features
Abstract
Background: To develop a predictive nomogram for breast cancer lympho-vascular invasion (LVI), based on digital breast tomography (DBT) data obtained from intra- and peri-tumoral regions.
Methods: One hundred ninety-two breast cancer patients were enrolled in this retrospective study from 2 institutions, in which Institution 1 served as the basis for training (n = 113) and testing (n = 49) sets, while Institution 2 served as the external validation set (n = 30). Tumor regions of interest (ROI) were manually-delineated on DBT images, in which peri-tumoral ROI was defined as 1 mm around intra-tumoral ROI. Radiomics features were extracted, and logistic regression was used to construct intra-, peri-, and intra- + peri-tumoral radiomics models. Patient clinical data was analyzed by both uni- and multi-variable logistic regression analyses to identify independent risk factors for the non-radiomics clinical imaging model, and the combination of both the most optimal radiomics and clinical imaging models comprised the comprehensive model. The best-performing model out of the 3 types (radiomics, clinical imaging, comprehensive) was identified using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis, and used to construct the predictive nomogram.
Results: The most optimal radiomics model was the intra- + peri-tumoral model, and 3 independent risk factors for LVI, maximum tumor diameter (odds ratio [OR] = 1.486, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 1.082-2.041, P = 0.014), suspicious malignant calcification (OR = 2.898, 95% CI = 1.232 ~ 6.815, P = 0.015), and axillary lymph node (ALN) metastasis (OR = 3.615, 95% CI = 1.642-7.962, P < 0.001) were identified by the clinical imaging model. Furthermore, the comprehensive model was the most accurate in predicting LVI occurrence, with areas under the curve (AUCs) of 0.889, 0.916, and 0.862, for, respectively, the training, testing and external validation sets, compared to radiomics (0.858, 0.849, 0.844) and clinical imaging (0.743, 0.759, 0.732). The resulting nomogram, incorporating radiomics from the intra- + peri-tumoral model, as well as maximum tumor diameter, suspicious malignant calcification, and ALN metastasis, had great correspondence with actual LVI diagnoses under the calibration curve, and was of high clinical utility under decision curve analysis.
Conclusions: The predictive nomogram, derived from both radiomics and clinical imaging features, was highly accurate in identifying future LVI occurrence in breast cancer, demonstrating its potential as an assistive tool for clinicians to devise individualized treatment regimes.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Digital breast tomography; Lympho-vascular invasion; Radiomics.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study protocol was approved by the ethics committees of the First Hospital of Shanxi Medical University (REB #:2023–174), and Shanxi Provincial People's Hospital (REB #:2022–344). The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. Written informed consent was provided by all patients. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

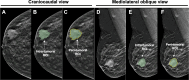



References
-
- Rakha EA, Abbas A, Pinto Ahumada P, ElSayed ME, Colman D, Pinder SE, Ellis IO. Diagnostic concordance of reporting lymphovascular invasion in breast cancer. J Clin Pathol. 2018;71(9):802–5. - PubMed
-
- Houvenaeghel G, Cohen M, Classe JM, Reyal F, Mazouni C, Chopin N, Martinez A, Daraï E, Coutant C, Colombo PE, et al. Lymphovascular invasion has a significant prognostic impact in patients with early breast cancer, results from a large, national, multicenter, retrospective cohort study. ESMO Open. 2021;6(6):100316. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sun Q, Chen Y, Liang C, Zhao Y, Lv X, Zou Y, Yan K, Zheng H, Liang D, Li ZC. Biologic pathways underlying prognostic radiomics phenotypes from Paired MRI and RNA sequencing in glioblastoma. Radiology. 2021;301(3):654–63. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 201803D31004/Shanxi Province key Research and Development Foundation
- 2023XM031/Four "Batches"Innovation Project of Invigorating Medical Through Science And Technology of Shanxi province
- 81900279/the Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2023-167-15/Pilot Base Construction Funding of Shanxi Province
- 20240044/the Scientific Activities of Selected Returned Overseas Professionals in Shanxi Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

