Effectiveness of an age-modified mindfulness-based cognitive therapy (MBCT) in improving mental health in older people with depressive symptoms: a non-randomised controlled trial
- PMID: 40011881
- PMCID: PMC11863447
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-025-04781-6
Effectiveness of an age-modified mindfulness-based cognitive therapy (MBCT) in improving mental health in older people with depressive symptoms: a non-randomised controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Emerging evidence has shown that mindfulness-based cognitive therapy (MBCT) is effective in improving depressive symptoms in the older population. However, the accessibility to MBCT is limited by the shortage of psychotherapists or mindfulness teachers. One potential solution is to involve social workers, who have the knowledge and skills to promote individual and community well-being in various settings, in delivering modified MBCT to enhance its accessibility and sustainability. This study examined the effectiveness of an eight-week age-modified MBCT led by different mental health professionals (mindfulness teacher only vs. mindfulness teacher and social worker) in improving mental health outcomes as compared with a control group.
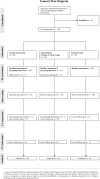
Methods: Older adults (N = 112) were recruited through five community-based centres for older adults and mental wellness in Hong Kong. Participants were allocated to one of three groups: (1) mindfulness teacher-led modified MBCT, (2) social worker/teacher co-led modified MBCT (50% led by social workers and 50% led by mindfulness teacher), or (3) control (care as usual). The age-modified MBCT consisted of eight weekly sessions, with age-related modifications including more sitting meditation, shortened duration of each session, and the removal of the retreat. Outcome variables (i.e., depressive symptoms, anxiety symptoms, perceived stress, and mindfulness) were assessed at baseline (T0), after the intervention (T1), and four weeks after the intervention (T2), through self-reported questionnaires. Linear mixed models were performed while controlling for demographic variables to examine changes in outcome variables between the groups.
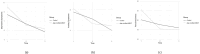
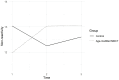
Results: Participants from the age-modified MBCT intervention groups (teacher-led and social worker/teacher co-led) showed significantly greater reductions in depressive symptoms and stress, as well as greater increase in mindful non-reactivity, compared to the control group post-intervention. No significant interaction effect of time and group was found for anxiety and both overall mindfulness and its other facets. The improvements in mental health and mindfulness outcomes post-intervention were not significantly different between the teacher-led and social worker/teacher co-led MCBT groups.
Discussion: Age-modified MBCT is beneficial in managing depressive and stress symptoms and in improving mindful non-reactivity among older adults at risk for depression. The findings support the feasibility and effectiveness of partial task-shifting in the delivery of MBCT to trained social workers. Future studies may explore the possibility for social workers in leading MBCTs independently to further improve its scalability and service accessibility for older adults in the community.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT05995587. Retrospectively registered on 16 August 2023.
Keywords: Anxiety; Depression; Mindfulness; Mindfulness-based cognitive therapy; Older adults; Social workers; Stress.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study was approved by the Human Research Ethics Committee (HREC) of the University of Hong Kong (Number: EA220105) on March 17, 2022. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants in the study. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Barberger-Gateau PFC. Disability and cognitive impairment in the elderly. Disabil Rehabil. 1997;19:175–93. - PubMed
-
- Naef RWR, Mahrer-Imhof R, Grande G. Characteristics of the bereavement experience of older persons after spousal loss: an integrative review. Int J Nurs Stud. 2013;50:1108–21. - PubMed
-
- Fiocco AJMS. The importance of cultivating mindfulness for cognitive and emotional well-being in late life. J Evidence-based Complement Altern Med. 2015;20:35–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

