The systemic inflammation response index as risks factor for all-cause and cardiovascular mortality among individuals with respiratory sarcopenia
- PMID: 40011897
- PMCID: PMC11863901
- DOI: 10.1186/s12890-025-03525-z
The systemic inflammation response index as risks factor for all-cause and cardiovascular mortality among individuals with respiratory sarcopenia
Abstract
Background: Respiratory sarcopenia is associated with poor outcomes, yet effective biomarkers for risk stratification remain limited. This study investigates the associations between complete blood count (CBC)-derived inflammatory biomarkers, including neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), neutrophil-monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio (NMLR), and systemic inflammation response index (SIRI) and both all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in patients with respiratory sarcopenia.
Methods: We conducted a cohort analysis of 1,673 adults with possible respiratory sarcopenia using data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) from 2007 to 2012, with mortality follow-up through December 31, 2019. Possible respiratory sarcopenia was assessed via peak expiratory flow rate (PEFR). Multivariable Cox regression models evaluated associations between NLR, NMLR, SIRI, and mortality outcomes, adjusted for demographic, socioeconomic, and health-related covariates. Additional CBC-derived biomarkers (PLR, dNLR, MLR, SII) were analysed, and mediation analysis assessed albumin's role as a partial mediator of mortality.
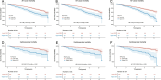
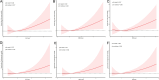
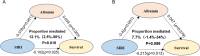
Results: Over a median follow-up of 116 months, 263 deaths occurred, including 68 from cardiovascular causes. Elevated NLR, NMLR, and SIRI were significantly associated with increased risks of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality. SIRI emerged as the strongest predictor, with adjusted hazard ratios (HRs) of 1.65 (95% CI, 1.23-2.22) for all-cause mortality and 3.18 (95% CI, 1.83-5.53) for cardiovascular mortality. Albumin partially mediated the relationship between SIRI and all-cause mortality (12.1%).
Conclusion: Elevated NLR, NMLR, and SIRI are associated with increased mortality risks in respiratory sarcopenia, with SIRI demonstrating the highest predictive power. Integrating SIRI into clinical assessments may aid in identifying high-risk patients, allowing for targeted interventions.
Keywords: All-cause mortality; Cardiovascular mortality; Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio; Neutrophil-to-monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio; Respiratory sarcopenia; Systemic inflammation response index.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Ethical clearance for the current study was granted by the National Center for Health Statistics Ethics Review Board, and all participants were required to provide written informed consent. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Associations of CBC-Derived inflammatory indicators with sarcopenia and mortality in adults: evidence from Nhanes 1999 ∼ 2006.BMC Geriatr. 2024 May 16;24(1):432. doi: 10.1186/s12877-024-05012-2. BMC Geriatr. 2024. PMID: 38755603 Free PMC article.
-
The relationship between complete blood cell count-derived inflammatory biomarkers and erectile dysfunction in the United States.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 30;14(1):32014. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-83733-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39738513 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative stress and inflammation mediate the adverse effects of cadmium exposure on all-cause and cause-specific mortality in patients with diabetes and prediabetes.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025 Mar 29;24(1):145. doi: 10.1186/s12933-025-02698-5. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025. PMID: 40158078 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Complete Blood Cell Count-Derived Inflammatory Biomarkers with Psoriasis and Mortality.Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2023 Nov 13;16:3267-3278. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S437936. eCollection 2023. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2023. PMID: 38021430 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic inflammatory biomarkers are novel predictors of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in individuals with osteoarthritis: a prospective cohort study using data from the NHANES.BMC Public Health. 2024 Jun 13;24(1):1586. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-19105-5. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38872115 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Correlation Between NLR to Albumin Ratio and 90-day Prognosis After Treatment for Acute Ischemic Stroke.J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2025 Jun 24. doi: 10.1007/s12265-025-10643-w. Online ahead of print. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2025. PMID: 40553383
References
-
- Kera T, Kawai H, Hirano H, Kojima M, Watanabe Y, Motokawa K, Fujiwara Y, Ihara K, Kim H, Obuchi S. Definition of Respiratory Sarcopenia With Peak Expiratory Flow Rate. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2019;20:1021–5. - PubMed
-
- Miyazaki S, Tamaki A, Wakabayashi H, Arai H. Definition, diagnosis, and treatment of respiratory sarcopenia. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2024;27:210–8. - PubMed
-
- Morisawa T, Kunieda Y, Koyama S, Suzuki M, Takahashi Y, Takakura T, Kikuchi Y, Matsuda T, Fujino Y, Sawa R, Sakuyama A, Saitoh M, Takahashi T, Fujiwara T. The Relationship between Sarcopenia and Respiratory Muscle Weakness in Community-Dwelling Older Adults. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18:13257. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

