Glioblastoma multiforme: insights into pathogenesis, key signaling pathways, and therapeutic strategies
- PMID: 40011944
- PMCID: PMC11863469
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-025-02267-0
Glioblastoma multiforme: insights into pathogenesis, key signaling pathways, and therapeutic strategies
Abstract
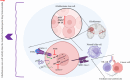
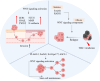
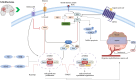
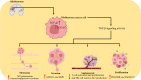
Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is the most prevalent and aggressive primary brain tumor in adults, characterized by a poor prognosis and significant resistance to existing treatments. Despite progress in therapeutic strategies, the median overall survival remains approximately 15 months. A hallmark of GBM is its intricate molecular profile, driven by disruptions in multiple signaling pathways, including PI3K/AKT/mTOR, Wnt, NF-κB, and TGF-β, critical to tumor growth, invasion, and treatment resistance. This review examines the epidemiology, molecular mechanisms, and therapeutic prospects of targeting these pathways in GBM, highlighting recent insights into pathway interactions and discovering new therapeutic targets to improve patient outcomes.
Keywords: Glioblastoma multiforme; Molecular mechanisms; Signaling pathways; Targeted therapy; Therapeutic resistance.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures








References
-
- Darlix A, et al. Epidemiology for primary brain tumors: a nationwide population-based study. J Neurooncol. 2017;131:525–46. - PubMed
-
- Tykocki T, Eltayeb M. Ten-year survival in glioblastoma. A systematic review. J Clin Neurosci. 2018;54:7–13. - PubMed
-
- Pouyan A, et al. Role of lncRNAs in brain tumors. Gene Reports. 2024;35(1):101904.
-
- Faleh TA, Juweid M. Epidemiology and outcome of Glioblastoma. Exon Publications, 2017: p. 143–153. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

