The promise of mesenchymal stromal/stem cells in erectile dysfunction treatment: a review of current insights and future directions
- PMID: 40012076
- PMCID: PMC11866689
- DOI: 10.1186/s13287-025-04221-9
The promise of mesenchymal stromal/stem cells in erectile dysfunction treatment: a review of current insights and future directions
Abstract
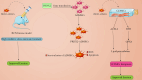
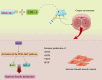
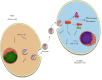
Erectile dysfunction is a common and multifactorial condition that significantly impacts men's quality of life. Traditional treatments, such as phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors (PDE5i), often fail to provide lasting benefits, particularly in patients with underlying health conditions. In recent years, regenerative medicine, particularly stem cell therapies, has emerged as a promising alternative for managing erectile dysfunction. This review explores the potential of mesenchymal stromal/stem cells (MSCs) and their paracrine effects, including extracellular vesicles (EVs), in the treatment of erectile dysfunction. MSCs have shown remarkable potential in promoting tissue repair, reducing inflammation, and regenerating smooth muscle cells, offering therapeutic benefits in models of erectile dysfunction. Clinical trials have demonstrated positive outcomes in improving erectile function and other clinical parameters. This review highlights the promise of MSC therapy for erectile dysfunction, discusses existing challenges, and emphasizes the need for continued research to refine these therapies and improve long-term patient outcomes.
Keywords: Erectile dysfunction; Exosomes; MSCs; Male infertility; Regeneration; Stem cell therapy.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors indicated no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
miR-200a-3p-enriched MSC-derived extracellular vesicles reverse erectile function in diabetic rats by targeting Keap1.Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 Aug;177:116964. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116964. Epub 2024 Jul 2. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 38959607
-
Improvement of damaged cavernosa followed by neuron-like differentiation at injured cavernous nerve after transplantation of stem cells seeded on the PLA nanofiber in rats with cavernous nerve injury.Mol Biol Rep. 2021 Apr;48(4):3549-3559. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06332-x. Epub 2021 Apr 17. Mol Biol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33866496
-
Transplantation of induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells improved erectile dysfunction induced by cavernous nerve injury.Theranostics. 2019 Aug 14;9(22):6354-6368. doi: 10.7150/thno.34008. eCollection 2019. Theranostics. 2019. PMID: 31588222 Free PMC article.
-
Strategies and Challenges of Mesenchymal Stem Cells-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Infertility.Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2024 Jun;30(3):385-403. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEB.2023.0094. Epub 2024 Apr 12. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2024. PMID: 38009217 Review.
-
Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms of the Therapeutic Effect of Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Extracellular Vesicles in Corneal Regeneration.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 16;25(20):11121. doi: 10.3390/ijms252011121. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39456906 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
High-activity placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells combined with low-intensity extracorporeal shock wave therapy for diabetic erectile dysfunction: a prospective randomized controlled trial.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025 Jul 9;16(1):359. doi: 10.1186/s13287-025-04499-9. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 40629484 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Hatzimouratidis K, Amar E, Eardley I, Giuliano F, Hatzichristou D, Montorsi F, Vardi Y, Wespes E. Guidelines on male sexual dysfunction: erectile dysfunction and premature ejaculation. Eur Urol. 2010;57:804–14. - PubMed
-
- Hadanny A, Lang E, Copel L, Meir O, Bechor Y, Fishlev G, Bergan J, Friedman M, Zisman A, Efrati S. Hyperbaric oxygen can induce angiogenesis and recover erectile function. Int J Impot Res. 2018;30:292–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

