Exploring bovine brucellosis in Bangladesh: Current scenario and future outlook
- PMID: 40013292
- PMCID: PMC11855437
- DOI: 10.5455/javar.2024.k840
Exploring bovine brucellosis in Bangladesh: Current scenario and future outlook
Abstract
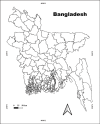
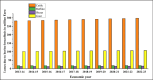
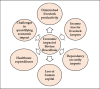
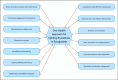
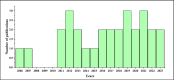
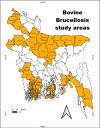
Bovine brucellosis is an enduring and formidable challenge in Bangladesh. In this first comprehensive review, we explored the historical, current, and future perspectives of bovine brucellosis outbreaks in Bangladesh. Data spanning from 1984 to 2023 regarding bovine brucellosis in Bangladesh were gathered from literature, reviews, conference papers, and online reports using various search engines and software tools. We considered 29 published documents and analyzed them thoroughly to evaluate the current status of bovine brucellosis for the present comprehensive review. We also suggest policy and other frameworks to mitigate and control the disease on a national scale. Bovine brucellosis in Bangladesh affects various livestock and poses economic burdens due to reduced milk and meat production with potential risks to human health. Over the past decade (2013-2023), the ruminant population in Bangladesh has increased substantially (between 1.46 and 26.95 million individuals), with goats showing the most significant growth, while financial losses due to bovine brucellosis have risen steadily, emphasizing its economic impact (basis on species between Euro currency 12.824 and 298.272). This review highlights brucellosis prevalence, diagnostic challenges, and traditional management practices contributing to its spread. Our findings indicate that bovine brucellosis was reported and prevalent in mild to severe forms across 26 districts of Bangladesh. Bangladesh has initiated measures such as vaccination and awareness campaigns, but effective control remains challenging due to diverse farming systems and resource constraints. A one-health approach is advocated for future strategies, emphasizing community engagement and multidisciplinary efforts to address the complex challenges posed by bovine brucellosis in Bangladesh, ultimately aiming to safeguard livestock health, public health, and economic stability.
Keywords: Control measures; economic impact; epidemiology; livestock health; one health approach; zoonotic disease.
© The authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Holt HR, Bedi JS, Kaur P, Mangtani P, Sharma NS, Gill JPS. Epidemiology of brucellosis in cattle and dairy farmers of rural Ludhiana, Punjab. PLoS Neglect Trop Dis. 2021;15(3):1–17. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0009102. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Islam S, Barua SR, Moni SP, Islam A, Rahman AKMA, Chowdhury S. Seroprevalence and risk factors for bovine brucellosis in the Chittagong Metropolitan Area of Bangladesh. Vet Med Sci. 2021;7(1):86–98. https://doi.org/10.1002/vms3.348. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mustafa AHM. Brucella antibodies in the sera of domestic livestock in Bangladesh. Trop Anim Health Prod. 1984;16(4):212. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02265323. - PubMed
-
- Amin KMR, Rahman MB, Rahman MS, Han JC, Park JH, Chae JS. Prevalence of Brucella antibodies in sera of cows in Bangladesh. J Vet Sci. 2005;6(3):223. https://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2005.6.3.223. - PubMed
-
- Akhtar J, Chowdhury OA, Das P, Sinha SP. Seroprevalence of human brucellosis among high risk and normal individuals of Sylhet district in Bangladesh. Bangladesh Med Res Coun Bull. 2020;46(1):35–40. https://doi.org/10.3329/bmrcb.v46i1.47467.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
