RNA vaccines: The dawn of a new age for tuberculosis?
- PMID: 40013818
- PMCID: PMC11869779
- DOI: 10.1080/21645515.2025.2469333
RNA vaccines: The dawn of a new age for tuberculosis?
Abstract
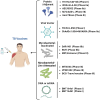
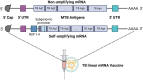
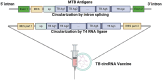
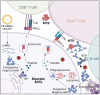
Since 2019, there has been a growing focus on mRNA vaccines for infectious disease prevention, particularly following the emergence of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). mRNA vaccines offer advantages such as rapid production and the ability to induce robust cellular and antibody responses, which are essential for combating infections that require cell-mediated immunity, including Tuberculosis (TB). This review explores recent progress in TB mRNA vaccines and addresses several key areas: (1) the urgent need for new TB vaccines; (2) current advancements in TB vaccine development, and the advantages and challenges of mRNA technology; (3) the design and characteristics of TB mRNA vaccines; (4) the immunological mechanisms of TB mRNA vaccines; (5) manufacturing processes for TB mRNA vaccines; and (6) safety and regulatory considerations. This interdisciplinary review aims to provide insights for researchers working to address critical questions in TB mRNA vaccine development.
Keywords: Mycobacterium tuberculosis; Tuberculosis; immunological mechanisms; mRNA vaccines; manufacture and quality control.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Novel mRNA vaccines induce potent immunogenicity and afford protection against tuberculosis.Front Immunol. 2025 Feb 13;16:1540359. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1540359. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40018046 Free PMC article.
-
Novel dual-pathogen multi-epitope mRNA vaccine development for Brucella melitensis and Mycobacterium tuberculosis in silico approach.PLoS One. 2024 Oct 28;19(10):e0309560. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0309560. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39466745 Free PMC article.
-
An LNP-mRNA vaccine modulates innate cell trafficking and promotes polyfunctional Th1 CD4+ T cell responses to enhance BCG-induced protective immunity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis.EBioMedicine. 2025 Mar;113:105599. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2025.105599. Epub 2025 Feb 15. EBioMedicine. 2025. PMID: 39955975 Free PMC article.
-
mRNA Vaccines: Design Principles, Mechanisms, and Manufacturing-Insights From COVID-19 as a Model for Combating Infectious Diseases.Biotechnol J. 2025 Feb;20(2):e202400596. doi: 10.1002/biot.202400596. Biotechnol J. 2025. PMID: 39989260 Review.
-
The current state of tuberculosis vaccines.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2013 Oct;9(10):2142-6. doi: 10.4161/hv.25427. Epub 2013 Jun 21. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2013. PMID: 23792698 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The synergistic role of viral infection and immune response in the pathogenesis of facial palsy.J Neurovirol. 2025 Jun;31(3):208-218. doi: 10.1007/s13365-025-01258-7. Epub 2025 May 15. J Neurovirol. 2025. PMID: 40374879 Review.
References
-
- Global tuberculosis report . World Health Organization; 2024.
-
- Almeida D, Converse PJ, Li SY, Upton AM, Fotouhi N, Nuermberger EL. Comparative efficacy of the novel diarylquinoline TBAJ-876 and bedaquiline against a resistant Rv0678 mutant in a mouse model of tuberculosis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2021;65(12):e0141221. doi:10.1128/AAC.01412-21. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
