TANGO2 is an acyl-CoA binding protein
- PMID: 40015245
- PMCID: PMC11867700
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.202410001
TANGO2 is an acyl-CoA binding protein
Abstract
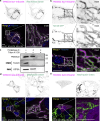
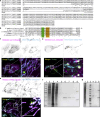
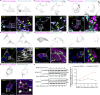
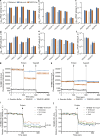
Loss of TANGO2 in humans precipitates metabolic crises during periods of heightened energy demand, such as fasting, infections, or high fever. TANGO2 has been implicated in various functions, including lipid metabolism and heme transport, and its cellular localization remains uncertain. In our study, we demonstrate that TANGO2 localizes to the mitochondrial lumen via a structural region containing LIL residues. Mutations in these LIL residues cause TANGO2 to relocate to the periphery of lipid droplets. We further show that purified TANGO2 binds acyl-coenzyme A, and mutations in the highly conserved NRDE sequence of TANGO2 inhibit this binding. Collectively, our findings suggest that TANGO2 serves as an acyl-coenzyme A binding protein. These insights may provide new avenues for addressing the severe cardiomyopathies and rhabdomyolysis associated with defective TANGO2 in humans.
© 2025 Lujan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: The authors declare no competing interests exist. Views and opinions expressed are however those of the author(s) only and do not necessarily reflect those of the European Union. Neither the European Union not the granting authority can be held responsible for them.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

