Cholesterol Granuloma Mimicking CSF Otorrhea by beta-Trace-Protein Production
- PMID: 40015730
- PMCID: PMC12105976
- DOI: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000004471
Cholesterol Granuloma Mimicking CSF Otorrhea by beta-Trace-Protein Production
Abstract
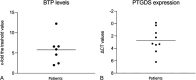
Objective: To report a patient who was misdiagnosed and operated on for cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) otorrhea and to demonstrate that cholesterol granulomas mimic CSF leakage by secreting beta-trace protein (BTP).
Patients: Eleven consecutive patients undergoing ear surgery in whom cholesterol granulomas were discovered intraoperatively.
Intervention: Biochemical and histologic analysis of liquid and solid fractions of cholesterol granulomas.
Main outcome measures: BTP and beta-2-transferrin concentrations and BTP mRNA levels in surgical specimens.
Results: Cholesterol granulomas produce BTP and express high levels of BTP mRNA, but do not produce beta-2-transferrin.
Conclusions: Beta-2 transferrin analysis is preferable to BTP analysis for the detection of CSF otorrhea because BTP may be false positive in the presence of cholesterol granulomas.
Keywords: Beta-trace-protein; CSF; Cholesterol granuloma; Granuloma; Liquorrhea.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of Otology & Neurotology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Oberascher G, Arrer E. First clinical experience with ß-2-transferrin in cerebrospinal fluid oto- and rhinoliquorrhea. HNO 1986;34:151–5. - PubMed
-
- Main TS, Shimada T, Lim DJ. Experimental cholesterol granuloma. Arch Otolaryngol 1970;91:356–9. - PubMed
-
- Lim DJ, Birck H. Ultrastructual pathology of the middle ear mucosa in serous otitis media. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 1971;80:838–53. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

