Patient-Reported Outcomes of Dental Implants in Type 2 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study on Quality of Life and Satisfaction
- PMID: 40018503
- PMCID: PMC11864912
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.78091
Patient-Reported Outcomes of Dental Implants in Type 2 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study on Quality of Life and Satisfaction
Abstract
Introduction: Dental implants provide a durable solution for missing teeth and improve mastication, speech, and quality of life (QoL). However, systemic conditions, such as type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), may affect implant success. This study evaluated patient satisfaction (PS) and QoL as patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs) following dental implant therapy in T2DM patients.
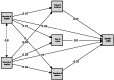
Materials and methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted in the Department of Prosthodontics on 90 T2DM patients who had undergone single-unit dental implant therapy at least one year prior to the study. Data were collected using validated PROMs tools, including the Oral Health Impact Profile-14 (OHIP-14) questionnaire for QoL and a nine-item PS questionnaire. Statistical analyses, including regression and mediation, were performed to identify predictors and relationships among the variables.
Results: The study reported moderate QoL scores (mean: 2.71 ± 0.61) and high PS scores (mean: 2.96 ± 0.44). Significant predictors of QoL included sex, implant duration, and implant survival, with successful implants showing a substantial positive association. Implant survival had the strongest direct impact on satisfaction, with ceramic crowns and anterior tooth positions being associated with higher scores. Mediation analysis revealed that factors such as crown type, duration of diabetes, and tooth loss period indirectly influenced outcomes. Implant survival remains the key determinant of both QoL and PS.
Conclusion: T2DM patients undergoing dental implant therapy exhibit moderate QoL and high PS, with implant survival being the most critical predictor of outcomes. Additional factors such as prosthetic choice, tooth position, and systemic health also play significant roles. These findings underscore the importance of glycemic control, individualized care, and robust implant planning to optimize outcomes in T2DM patients.
Keywords: dental implants; diabetes mellitus type 2; patient satisfaction; quality of life; questionnaire.
Copyright © 2025, Davangere et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Institutional Ethical Committee of Sharda University issued approval SU/SMS&R/76-A/2023/34. The study adhered to the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki and was conducted by anonymizing all patient data. Animal subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve animal subjects or tissue. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures

References
-
- Marginal bone loss of dental implants in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus with poorly controlled HbA1c values: a long-term retrospective study. Lorean A, Ziv-On H, Perlis V, Ormianer Z. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33909727/ Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2021;36:355–360. - PubMed
-
- The effect of moderately controlled type 2 diabetes on dental implant survival and peri-implant bone loss: a long-term retrospective study. Ormianer Z, Block J, Matalon S, Kohen J. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29534127/ Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2018;33:389–394. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
