Pirtobrutinib in Chinese patients with relapsed or refractory B-cell malignancies: A single-arm, open-label, phase 2, multicenter trial
- PMID: 40018797
- PMCID: PMC11970546
- DOI: 10.1002/ijc.35339
Pirtobrutinib in Chinese patients with relapsed or refractory B-cell malignancies: A single-arm, open-label, phase 2, multicenter trial
Abstract
Pirtobrutinib, a highly selective, noncovalent (reversible) Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor (BTKi), demonstrated clinically meaningful antitumor responses in covalent BTKi pretreated mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL) in the global phase 1/2 BRUIN study. In this multi-center, open-label, phase 2 trial, we investigated the efficacy and safety of pirtobrutinib in Chinese patients with BTKi pretreated relapsed/refractory (R/R) MCL, CLL/SLL, or other B-cell malignancies. All patients received pirtobrutinib once daily in continuous 28-day cycles. The primary endpoint was the overall response rate (ORR). Efficacy was assessed in patients with MCL and CLL/SLL with prior BTKi treatment and safety in all enrolled patients who received at least one dose of pirtobrutinib. Among 35 patients with covalent BTKis (cBTKi) pretreated MCL, the ORR was 62.9% (95% CI: 44.9, 78.5), the median duration of response (DOR) was not reached, and the 12-month DOR rate was 59.7% (95% CI: 35.3, 77.5). Among 11 patients with cBTKi pretreated CLL/SLL, the ORR was 63.6% (95% CI: 30.8, 89.1), and the 12-month DOR rate was 83.3% (95% CI: 27.3, 97.5). The most common adverse events in the safety population (n = 87) were anemia (32.2%) and neutrophil count decreased (31.0%). Grade ≥3 hemorrhage occurred in 2.3% of patients and there were no cases of atrial fibrillation/flutter. Pirtobrutinib demonstrated clinically meaningful efficacy in Chinese patients with cBTKi pretreated R/R MCL, preliminary antitumor activity in Chinese patients with cBTKi pretreated R/R CLL/SLL and was generally well-tolerated with no new safety signals observed.
Keywords: chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma; mantle cell lymphoma; noncovalent BTK inhibitor; pirtobrutinib.
© 2025 Eli Lilly and Company and The Author(s). International Journal of Cancer published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of UICC.
Conflict of interest statement
YQ and JZ are employees of and shareholders in Eli Lilly and Company. The other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
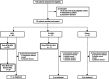
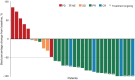
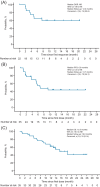
References
-
- Jain P, Wang ML. Mantle cell lymphoma in 2022—a comprehensive update on molecular pathogenesis, risk stratification, clinical approach, and current and novel treatments. Am J Hematol. 2022;97:638‐656. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization . GLOBOCAN 2022. Population Fact Sheets. WHO; 2022.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

