Neural stem cell relay from B1 to B2 cells in the adult mouse ventricular-subventricular zone
- PMID: 40019835
- PMCID: PMC11979704
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2025.115264
Neural stem cell relay from B1 to B2 cells in the adult mouse ventricular-subventricular zone
Abstract
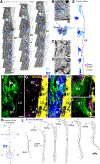
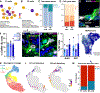
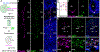
Neurogenesis and gliogenesis continue in the ventricular-subventricular zone (V-SVZ) of the adult rodent brain. V-SVZ astroglial cells with apical contact with the ventricle (B1 cells) function as neural stem cells (NSCs). B1 cells sharply decline during early postnatal life; in contrast, neurogenesis decreases at a slower rate. Here, we show that a second population of astroglia (B2 cells) that do not contact the ventricle also function as NSCs in the adult mouse brain. B2 cell numbers increase postnatally, are sustained in adults, and decrease with aging. We reveal the transcriptomic profile of B1 and B2 cells and show that, like B1 cells, B2 cells can be quiescent or activated. Transplantation and lineage tracing of B2 cells demonstrate their function as primary progenitors for adult neurogenesis. This study reveals that NSC function is progressively relayed from B1 to B2 progenitors helping explain how neurogenesis is maintained into adult life.
Keywords: B1 cells; B2 cells; CP: Neuroscience; apical cells; basal cells; neural stem cells; neurogenesis; primary cilium; transcriptomics; ventricular-subventricular zone; wedge region.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests A.A.-B. is the Heather and Melanie Muss Endowed Chair and Professor of Neurological Surgery at UCSF. He is co-founder and on the Scientific Advisory Board of Neurona Therapeutics.
Figures



Update of
-
Neural Stem Cell Relay from B1 to B2 cells in the adult mouse Ventricular-Subventricular Zone.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jul 9:2024.06.28.600695. doi: 10.1101/2024.06.28.600695. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Cell Rep. 2025 Mar 25;44(3):115264. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2025.115264. PMID: 39005355 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

