Estrogen receptor β stimulation as a possible novel therapeutic target for cutaneous T-cell lymphoma
- PMID: 40020159
- PMCID: PMC12155627
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2024015132
Estrogen receptor β stimulation as a possible novel therapeutic target for cutaneous T-cell lymphoma
Abstract
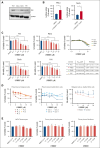
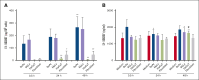
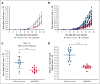
Cutaneous T-cell lymphomas (CTCLs), including mycosis fungoides (MF) and Sézary syndrome (SS), are rare hematological malignancies with limited curative treatment options. Despite early-stage responsiveness, these malignancies often relapse in advanced stages, highlighting the need for novel, durable therapies. Similar to other non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs), MF and SS have a greater incidence rate in males than females. The endocrine contribution to this sex difference is unknown. Although several studies could show a potential role of estrogen receptor β (ERβ) on NHL lymphomagenesis, its impact on CTCL development is unknown. In this study, we investigated LY500307, a selective ERβ agonist, as a potential treatment for CTCL. Our results show that LY500307 selectively reduced the viability of CTCL cells, sparing noncancerous skin cells. Liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry analysis revealed that CTCL cells accumulated significantly higher concentrations of LY500307 than normal skin cells, likely contributing to its selective cytotoxicity. Mechanistically, LY500307 induced apoptosis, G2/M cell cycle arrest, and increased sensitivity to chemotherapeutic agents, particularly Monomethyl auristatin E. Furthermore, LY500307 treatment significantly reduced tumor growth in a CTCL xenograft mouse model without notable toxicity. These findings suggest LY500307 as a promising therapeutic agent for CTCL, warranting further clinical investigation, including the potential for topical applications.
© 2025 American Society of Hematology. Published by Elsevier Inc. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures



References
-
- Mourad A, Gniadecki R. Overall survival in mycosis fungoides: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Invest Dermatol. 2020;140(2):495–497.e5. - PubMed
-
- Afifi S, Mohamed S, Zhao J, Foss F. A drug safety evaluation of mogamulizumab for the treatment of cutaneous T-Cell lymphoma. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2019;18(9):769–776. - PubMed
-
- Dippel E, Assaf C, Becker JC, et al. S2k guidelines - cutaneous lymphomas update 2016 - part 2: treatment and follow-up (ICD10 C82 - C86) J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2018;16(1):112–122. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

