Challenging Conventional Diagnostic Methods by Comprehensive Molecular Diagnostics: A Nationwide Prospective Comparison in Children With ALL
- PMID: 40020210
- PMCID: PMC11913173
- DOI: 10.1200/PO-24-00788
Challenging Conventional Diagnostic Methods by Comprehensive Molecular Diagnostics: A Nationwide Prospective Comparison in Children With ALL
Abstract
Purpose: Treatment stratification in ALL includes diverse (cyto)genetic aberrations, requiring diverse tests to yield conclusive data. We optimized the diagnostic workflow to detect all relevant aberrations with a limited number of tests in a clinically relevant time frame.
Methods: In 467 consecutive patients with ALL (0-20 years), we compared RNA sequencing (RNAseq), fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), karyotyping, single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) array, and multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA) for technical success, concordance of results, and turnaround time.
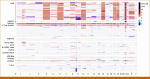
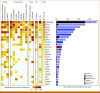
Results: To detect stratifying fusions (ETV6::RUNX1, BCR::ABL1, ABL-class, KMT2Ar, TCF3::HLF, IGH::MYC), RNAseq and FISH were conclusive for 97% and 96% of patients, respectively, with 99% concordance. RNAseq performed well in samples with a low leukemic cell percentage or low RNA quality. RT-PCR for six specific fusions was conclusive for >99% but false-negative for six patients with alternatively fused exons. RNAseq also detected gene fusions not yet used for stratification in 14% of B-cell precursor-ALL and 33% of T-ALL. For aneuploidies and intrachromosomal amplification of chromosome 21, SNP array gave a conclusive result in 99%, thereby outperforming karyotyping, which was conclusive for 64%. To identify deletions in eight stratifying genes/regions, SNP array was conclusive in 99% and MLPA in 95% of patients, with 98% concordance. The median turnaround times were 10 days for RNAseq, 9 days for FISH, 10 days for SNP array, and <7 days for MLPA and RT-PCR in this real-world prospective study.
Conclusion: Combining RNAseq and SNP array outperformed current diagnostic tools to detect all stratifying genetic aberrations in ALL. The turnaround time is <15 days matching major treatment decision time points. Moreover, combining RNAseq and SNP array has the advantage of detecting new lesions for studies on prognosis and pathobiology.
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
Figures


References
-
- Biondi A, Gandemer V, De Lorenzo P, et al. : Imatinib treatment of paediatric Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (EsPhALL2010): A prospective, intergroup, open-label, single-arm clinical trial. Lancet Haematol 5:e641-e652, 2018 - PubMed
-
- Pieters R, de Groot-Kruseman H, Fiocco M, et al. : Improved outcome for ALL by prolonging therapy for IKZF1 deletion and decreasing therapy for other risk groups. J Clin Oncol 41:4130-4142, 2023 - PubMed
-
- Pieters R, de Groot-Kruseman H, Van der Velden V, et al. : Successful therapy reduction and intensification for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia based on minimal residual disease monitoring: Study ALL10 from the Dutch Childhood Oncology Group. J Clin Oncol 34:2591-2601, 2016 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

