Analysis of Stratifin Expression and Proteome Variation in a Rat Model of Acute Lung Injury
- PMID: 40021485
- PMCID: PMC11976852
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.4c00980
Analysis of Stratifin Expression and Proteome Variation in a Rat Model of Acute Lung Injury
Abstract
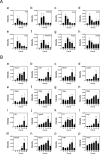
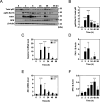
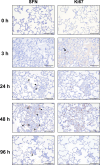
Diffuse alveolar damage (DAD) is a pathological hallmark of severe interstitial lung diseases, such as acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), and is linked to poor prognosis. Previously, we identified 14-3-3σ/stratifin (SFN) as a serum biomarker candidate for diagnosing DAD. To clarify the time-dependent relationship between SFN expression and DAD, we here investigated pathological and molecular changes in serum, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF), and lung tissue in an oleic acid (OA)-induced ARDS rat model. Acute alveolar edema was observed after OA administration, followed by alveolar epithelial cell proliferation and increased BALF and serum SFN levels. Proteomic analysis of lung tissue extracts revealed that proteins related to "inflammatory response" and "HIF-1 signaling," including plasminogen activator inhibitor-1, were markedly increased 3 h after acute lung injury, followed by a gradual decrease. Conversely, proteins associated with "cell cycle" and "p53 pathway," including SFN, showed a persistent increase starting at 3 h and peaking at 48 h. Western blotting and immunohistochemistry confirmed that SFN was expressed in a part of proliferated alveolar type-II cells, accompanied by p53 activation, an important event for differentiation into type-I cells. SFN may be a biomarker closely related to alveolar remodeling during the repair process after lung injury.
Keywords: acute lung injury; acute respiratory distress syndrome; biomarker; diffuse alveolar damage; interstitial lung disease; oleic acid; proteomics; stratifin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
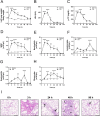
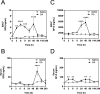
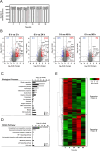
References
-
- Kawase S.; Hattori N.; Ishikawa N.; Horimasu Y.; Fujitaka K.; Furonaka O.; Isobe T.; Miyoshi S.; Hamada H.; Yamane T.; et al. Change in serum KL-6 level from baseline is useful for predicting life-threatening EGFR-TKIs induced interstitial lung disease. Respir Res. 2011, 12 (1), 97.10.1186/1465-9921-12-97. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arakawa N.; Matsuyama S.; Matsuoka M.; Kitamura I.; Miyashita K.; Kitagawa Y.; Imai K.; Ogawa K.; Maeda T.; Saito Y.; Hasegawa C. Serum stratifin and presepsin as candidate biomarkers for early detection of COVID-19 disease progression. J. Pharmacol Sci. 2022, 150 (1), 21–30. 10.1016/j.jphs.2022.06.002. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sakuma N.; Abe M.; Ishii D.; Kawasaki T.; Arakawa N.; Matsuyama S.; Saito Y.; Suzuki T.; Tatsumi K. Serum stratifin measurement is useful for evaluating disease severity and outcomes in patients with acute exacerbation of interstitial lung disease: a retrospective study. BMC Pulm Med. 2024, 24 (1), 364.10.1186/s12890-024-03184-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

