GWAS meta-analysis of psoriasis identifies new susceptibility alleles impacting disease mechanisms and therapeutic targets
- PMID: 40021644
- PMCID: PMC11871359
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-56719-8
GWAS meta-analysis of psoriasis identifies new susceptibility alleles impacting disease mechanisms and therapeutic targets
Abstract
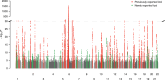
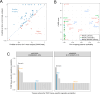
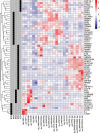
Psoriasis is a common, debilitating immune-mediated skin disease. Genetic studies have identified biological mechanisms of psoriasis risk, including those targeted by effective therapies. However, the genetic liability to psoriasis is not fully explained by variation at robustly identified risk loci. To refine the genetic map of psoriasis susceptibility we meta-analysed 18 GWAS comprising 36,466 cases and 458,078 controls and identified 109 distinct psoriasis susceptibility loci, including 46 that have not been previously reported. These include susceptibility variants at loci in which the therapeutic targets IL17RA and AHR are encoded, and deleterious coding variants supporting potential new drug targets (including in STAP2, CPVL and POU2F3). We conducted a transcriptome-wide association study to identify regulatory effects of psoriasis susceptibility variants and cross-referenced these against single cell expression profiles in psoriasis-affected skin, highlighting roles for the transcriptional regulation of haematopoietic cell development and epigenetic modulation of interferon signalling in psoriasis pathobiology.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: F.C. reports grants and consultancy fees from Boehringer Ingelheim. S.K.M. reports departmental income from Abbvie, Almirall, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Leo Pharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi and UCB, outside the submitted work. M.J.N. has received consultancy fees and/or research funding from Abbvie, Amgen, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Pfizer, Novartis and UCB. T. T. serves on an advisory board for L’Oreal Teledermatology. V.C. has received research grants from AbbVie, Amgen, and Eli Lilly and has received honoraria for advisory board member roles from AbbVie, Amgen, BMS, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB. His spouse is an employee of AstraZeneca. D.D.G. received grant support and/or consulting fees from Abbvie, Amgen, BMS, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer and UCB. J.E.G. received research support from Eli Lilly, Kyowa Kirin, Janssen, Almirall, Celgene/BMS, Prometheus, Novartis, Galderma and AnaptysBio, and is a member of an advisory board for Novartis, AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Almirall, Galderma, Boehringer Ingelehim, Celgene/BMS, Sanofi, Janssen and AnaptysBio. S.K. is a founder of Prion OÜ, Geneto OÜ, Sportsgene OÜ and Genomic Therapeutics Pty Ltd. W.L. has received research grant funding from Abbvie, Amgen, Janssen, Leo, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, and TRex Bio. P.D.M. reports consultancy fees from Unilever and speaker’s fees from Sanofi and BMS. L.C.T. reports support from Janssen, Galderma, and Novartis. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Update of
-
GWAS meta-analysis of psoriasis identifies new susceptibility alleles impacting disease mechanisms and therapeutic targets.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Oct 5:2023.10.04.23296543. doi: 10.1101/2023.10.04.23296543. medRxiv. 2023. Update in: Nat Commun. 2025 Feb 28;16(1):2051. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-56719-8. PMID: 37873414 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Griffiths, C. E. M., Armstrong, A. W., Gudjonsson, J. E. & Barker, J. N. W. N. Psoriasis. Lancet397, 1301–1315 (2021). - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Global Report on Psoriasis. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/204417, (World Health Organization, 2016).
-
- Brezinski, E. A., Dhillon, J. S. & Armstrong, A. W. Economic burden of psoriasis in the United States: a systematic review. JAMA Dermatol151, 651–658 (2015). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 ES033634/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01AR050511, R01AR054966, R01AR063611, R01AR065183/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- BRC_1215_20006, NIHR302258, NIHR203308, BRC-1215-20014/DH | National Institute for Health Research (NIHR)
- 980/Maudsley Charity
- RG2/10, ST1/19, ST3/20/Psoriasis Association
- EXC 2167-390884018, CRC1181-2/project A05/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- STR130505/Guy's and St Thomas' Charity
- K01 AR072129, P30 AR075043, UC2 AR081033, R01AR042742/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- K08 AR078251/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR075043/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AR072129/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- 814364/National Psoriasis Foundation (NPF)
- R01 AR042742/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- PUT1465, PRG1189, PRG1911, PRG1291/Eesti Teadusagentuur (Estonian Research Council)
- 2014-2020.4.01.15-0012/EC | European Regional Development Fund (Europski Fond za Regionalni Razvoj)
- U01AI119125/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- LF-OC-22-001033/LEO Pharma Research Foundation
- 821511/Innovative Medicines Initiative (IMI)
- RG-1611-26299/National Multiple Sclerosis Society (National MS Society)
- MR/S003126/1/RCUK | Medical Research Council (MRC)
- U01 AI119125/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01ES033634, R35GM138121, K08 AR078251, R01AR065174/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01 AR054966/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR050511/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR065174/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM138121/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 01EC1407A, 01EC1401C/Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (Federal Ministry of Education and Research)
- SI 236/8-1, SI236/9-1, ER 155/6-1/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- UC2 AR081033/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR065183/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR063611/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States

