ACSS2 drives senescence-associated secretory phenotype by limiting purine biosynthesis through PAICS acetylation
- PMID: 40021646
- PMCID: PMC11871226
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-57334-3
ACSS2 drives senescence-associated secretory phenotype by limiting purine biosynthesis through PAICS acetylation
Abstract
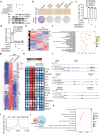
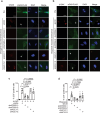
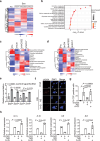
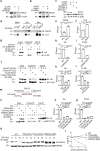
Senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) mediates the biological effects of senescent cells on the tissue microenvironment and contributes to ageing-associated disease progression. ACSS2 produces acetyl-CoA from acetate and epigenetically controls gene expression through histone acetylation under various circumstances. However, whether and how ACSS2 regulates cellular senescence remains unclear. Here, we show that pharmacological inhibition and deletion of Acss2 in mice blunts SASP and abrogates the pro-tumorigenic and immune surveillance functions of senescent cells. Mechanistically, ACSS2 directly interacts with and promotes the acetylation of PAICS, a key enzyme for purine biosynthesis. The acetylation of PAICS promotes autophagy-mediated degradation of PAICS to limit purine metabolism and reduces dNTP pools for DNA repair, exacerbating cytoplasmic chromatin fragment accumulation and SASP. Altogether, our work links ACSS2-mediated local acetyl-CoA generation to purine metabolism through PAICS acetylation that dictates the functionality of SASP, and identifies ACSS2 as a potential senomorphic target to prevent senescence-associated diseases.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Lopez-Otin, C., Blasco, M. A., Partridge, L., Serrano, M. & Kroemer, G. Hallmarks of aging: An expanding universe. Cell186, 243–278 (2023). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

