Lipid-lowering therapy and LDL target attainment in type 2 diabetes: trends from the Italian Associations of Medical Diabetologists database
- PMID: 40022078
- PMCID: PMC11871825
- DOI: 10.1186/s12933-025-02648-1
Lipid-lowering therapy and LDL target attainment in type 2 diabetes: trends from the Italian Associations of Medical Diabetologists database
Abstract
Background: Hypercholesterolemia is a major cardiovascular risk factor, particularly in individuals with type 2 diabetes (T2DM), where cardiovascular events are more prevalent. Adherence to low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-c) targets remains suboptimal globally and in Italy. This study evaluates trends in LDL-c target achievement and lipid-lowering treatment with a stratification by cardiovascular risk among Italian patients with type 2 diabetes from 2019 to 2022.
Methods: A cross-sectional analysis was conducted using the AMD Annals database, encompassing over 700,000 patients with T2DM. Patients were categorized by cardiovascular risk levels, LDL-c ranges and therapy types (statins, ezetimibe, PCSK9 inhibitors). Linear trends across the four years were evaluated.
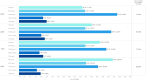
Results: The percentage of patients achieving LDL-c targets improved across all risk levels. In very high-risk patients, LDL-c < 55 mg/dL was achieved by 16.3% in 2019, increasing to 23.6% in 2022. High-risk patients achieving LDL-c < 70 mg/dL rose from 20.3 to 26.6% over the same period. Use of PCSK9 inhibitors, particularly in combination with statins, was associated with the highest target achievement rates, reaching 62% in very high-risk patients by 2022. We observed a reduction of moderate-intensity statins use in favor of combination therapies across the four years. Despite this, nearly one-third of patients still had LDL-c levels ≥ 100 mg/dL in 2022.
Conclusions: While LDL-c management in Italian patients with T2DM has improved, significant gaps remain, particularly for very high-risk individuals. Expanding the use of advanced therapies like PCSK9 inhibitors and adhering more closely to guideline-based recommendations are critical to improve cardiovascular risk in this population.
Keywords: Cardiovascular risk; Hypercholesterolemia; LDL cholesterol; Lipid-lowering therapy; PCSK9 inhibitors; Statins; Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and all participating diabetes centers obtained the authorization of local Ethics Committees. All data were anonymized, and no direct patient involvement was required, ensuring compliance with ethical standards and data protection regulations. Consent for publication: According to Italian Law 211/2003, no consent is required for epidemiological analysis regarding anonymous data. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Mooradian AD. Cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus: current management guidelines. Arch Intern Med. 2003;163:33. 10.1001/archinte.163.1.33. - PubMed
-
- Borén J, Chapman MJ, Krauss RM, Packard CJ, Bentzon JF, Binder CJ, et al. Low-density lipoproteins cause atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: pathophysiological, genetic, and therapeutic insights: a consensus statement from the European Atherosclerosis Society Consensus Panel. Eur Heart J. 2020;41:2313–30. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

