Short- and long-term comparative effectiveness of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir and molnupiravir in asthma patients: a cohort study
- PMID: 40022135
- PMCID: PMC11871785
- DOI: 10.1186/s12931-025-03156-2
Short- and long-term comparative effectiveness of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir and molnupiravir in asthma patients: a cohort study
Abstract
Background: Few studies evaluated the effectiveness of COVID-19 antivirals specifically in the asthma population This study assessed short- and long-term effects of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir versus molnupiravir in asthma population.
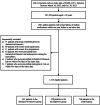
Methods: This is a retrospective cohort study on adult asthma patients infected with COVID-19, using real-world data obtained from the health officials in Hong Kong. Key inclusion criteria were infection with COVID-19 between March 16, 2022, and Oct 30, 2023, age ≥ 18 years, previous asthma diagnosis, and prescription history of an asthma medication. Outcomes included acute and post-acute mortality, post-acute all-cause hospitalization, and cause-specific hospitalization.
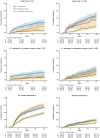
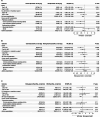
Results: 1,745 patients were eligible for this study, with a median follow-up time of 365 days (IQR: 335-365). Patients in the nirmatrelvir/ritonavir group had significantly lower risks of acute inpatient death (HR, 0·27 [95% CI, 0·12 to 0·59]; p = 0·0011), post-acute inpatient death (HR, 0·49 [95% CI, 0·28 to 0·85]; p = 0·011), all-cause hospitalization (HR, 0·72 [95% CI, 0·58 to 0·89]; p = 0·0020), and myocardial infarction (HR, 0·10 [95% CI, 0·01 to 0·92]; p = 0·042) than patients in the control group. The risk of all-cause hospitalization was significantly lower in the nirmatrelvir/ritonavir group compared to the molnupiravir group (HR, 0·65 [95% CI, 0·52 to 0·81]; p = 0·00012). Among patients who were prescribed medium-/ high-dose inhaled corticosteroids, the nirmatrelvir/ritonavir group had a lower hazard of asthma exacerbation than the molnupiravir group (HR, 0·58 [95% CI, 0·35 to 0·95]; p = 0.030).
Conclusion: Compared with molnupiravir, nirmatrelvir/ritonavir may offer more benefits in reducing the risk of post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 among asthma patients. In addition, the post-acute benefits of the antivirals were also demonstrated in patients with mild asthma, which have not been generally recommended in existing clinical management guidelines.
Keywords: Asthma; COVID-19; Effectiveness; Molnupiravir; Nirmatrelvir/ritonavir.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Ethics approval was obtained from the Joint CUHK-NTEC Clinical Research Ethics Committee (2023.006). As this study was a retrospective analysis using secondary data without any personal information, the requirement for obtaining informed consent was waived. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Clinical trial number: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Fact sheet for healthcare providers: emergency use authorization for Paxlovid™. Time last updated: Sep 2024. Time last accessed: Sep 23 2024. www.fda.gov/media/155050/download
-
- Fact sheet for healthcare providers: emergency use authorization for Lagevrio™ (molnupiravir) capsules. Time last updated: June 2024. Time last accessed: Sep 23 2024. www.fda.gov/media/155054/download
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

