Relationship between atherogenic index of plasma and length of stay in critically ill patients with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: a retrospective cohort study and predictive modeling based on machine learning
- PMID: 40022165
- PMCID: PMC11871731
- DOI: 10.1186/s12933-025-02654-3
Relationship between atherogenic index of plasma and length of stay in critically ill patients with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: a retrospective cohort study and predictive modeling based on machine learning
Abstract
Background: The atherogenic index of plasma (AIP) is considered an important marker of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular risk. However, its potential role in predicting length of stay (LOS), especially in patients with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD), remains to be explored. We investigated the effect of AIP on hospital LOS in critically ill ASCVD patients and explored the risk factors affecting LOS in conjunction with machine learning.
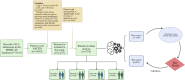
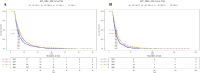
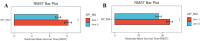
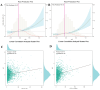
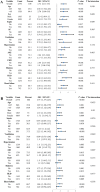
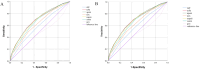
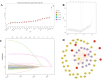
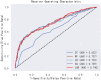
Methods: Using data from the Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care (MIMIC)-IV. AIP was calculated as the logarithmic ratio of TG to HDL-C, and patients were stratified into four groups based on AIP values. We investigated the association between AIP and two key clinical outcomes: ICU LOS and total hospital LOS. Multivariate logistic regression models were used to evaluate these associations, while restricted cubic spline (RCS) regressions assessed potential nonlinear relationships. Additionally, machine learning (ML) techniques, including logistic regression (LR), decision tree (DT), random forest (RF), extreme gradient boosting (XGB), and light gradient boosting machine (LGB), were applied, with the Shapley additive explanation (SHAP) method used to determine feature importance.
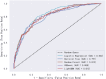
Results: The study enrolled a total of 2423 patients with critically ill ASCVD, predominantly male (54.91%), and revealed that higher AIP values were independently associated with longer ICU and hospital stays. Specifically, for each unit increase in AIP, the odds of prolonged ICU and hospital stays were significantly higher, with adjusted odds ratios (OR) of 1.42 (95% CI, 1.11-1.81; P = 0.006) and 1.73 (95% CI, 1.34-2.24; P < 0.001), respectively. The RCS regression demonstrated a linear relationship between increasing AIP and both ICU LOS and hospital LOS. ML models, specifically LGB (ROC:0.740) and LR (ROC:0.832) demonstrated superior predictive accuracy for these endpoints, identifying AIP as a vital component of hospitalization duration.
Conclusion: AIP is a significant predictor of ICU and hospital LOS in patients with critically ill ASCVD. AIP could serve as an early prognostic tool for guiding clinical decision-making and managing patient outcomes.
Keywords: AIP; Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease; LOS; MIMIC-IV; Machine learning.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study was an analysis of a third-party anonymized publicly available database with pre-existing institutional review board (IRB) approval. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Balakumar P, Maung UK, Jagadeesh G. Prevalence and prevention of cardiovascular disease and diabetes mellitus. Pharmacol Res. 2016;113(Pt A):600–9. - PubMed
-
- Chen W, Thomas J, Sadatsafavi M, FitzGerald JM. Risk of cardiovascular comorbidity in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Respir Med. 2015;3(8):631–9. - PubMed
-
- Hu P, Dharmayat KI, Stevens CAT, Sharabiani MTA, Jones RS, Watts GF, Genest J, Ray KK, Vallejo-Vaz AJ. Prevalence of Familial hypercholesterolemia among the general population and patients with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Circulation. 2020;141(22):1742–59. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

