Association between triglyceride-glucose related indices and all-cause and cardiovascular mortality among the population with cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic syndrome stage 0-3: a cohort study
- PMID: 40022225
- PMCID: PMC11871745
- DOI: 10.1186/s12933-025-02642-7
Association between triglyceride-glucose related indices and all-cause and cardiovascular mortality among the population with cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic syndrome stage 0-3: a cohort study
Abstract
Background: Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic (CKM) syndrome typically commences with the interaction of insulin resistance (IR), excessive or dysfunctional obesity, and the consequent systemic inflammatory response and oxidative stress. The relationship between the triglyceride-glucose (TyG) index and TyG-related indices that may simply assess IR and obesity, as well as the mortality risk in the CKM syndrome population, remains ambiguous.
Methods: This study included 6,383 participants from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2009-2018. The TyG index, TyG-waist-to-height ratio (TyG-WHtR), TyG-waist circumference (TyG-WC), and TyG-body mass index (TyG-BMI) were developed. Cox proportional hazards models, smooth curve fitting, and two-stage Cox proportional hazards models were employed to examine the association of TyG and TyG-related indices with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in the CKM syndrome population. Subgroup analyses and interaction tests were conducted to evaluate the risk within various demographics.
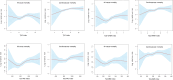
Results: In survey-weighted multifactorial regression analyses, a significant positive association existed between TyG, TyG-related indices, and both all-cause mortality and cardiovascular mortality, except for the TyG index, which did not demonstrate a significant link with all-cause mortality. Of these indices, the TyG-WC index exhibited the strongest correlation with all-cause mortality, with a hazard ratio (HR) of 1.50 and a 95% confidence interval (CI) of 1.18-1.92, followed by the TyG-WHtR index (HR: 1.45, 95%CI 1.13-1.85). The TyG-WHtR index demonstrated the strongest correlation with cardiovascular mortality (HR: 1.85, 95% CI 1.19-2.86), followed by the TyG-WC index(HR: 1.83, 95%CI 1.21-2.78). An L-shaped association was identified between TyG-WHtR, TyG-BMI, and all-cause mortality in CKM syndrome during the examination of nonlinear relationships (both P for log-likelihood ratio < 0.05). The TyG-WHtR, TyG-WC, and TyG-BMI indices exhibited a more pronounced correlation with all-cause mortality in those with CKM syndrome stages 1 and 3 (P value < 0.05, P for interaction < 0.05).
Conclusion: Our study emphasizes the association between TyG and TyG-related indices and mortality in individuals with CKM syndrome stages 0-3. Individuals with CKM syndrome stages 1 and 3 should be more vigilant to abnormal alterations in TyG-related indices.
Keywords: All-cause mortality; Body mass index; Cardiovascular mortality; Cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic syndrome; Triglyceride-glucose index; Waist circumference; Waist-to-height ratio.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The NHANES study protocol received approval from the Ethics Review Board of the National Center for Health Statistics. All participants executed a written informed consent form before their involvement. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Ndumele CE, Neeland IJ, Tuttle KR, Chow SL, Mathew RO, Khan SS, et al. A synopsis of the evidence for the science and clinical management of cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic (CKM) syndrome: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2023;148(20):1636–64. - PubMed
-
- Packham DK, Alves TP, Dwyer JP, Atkins R, de Zeeuw D, Cooper M, et al. Relative incidence of ESRD versus cardiovascular mortality in proteinuric type 2 diabetes and nephropathy: results from the DIAMETRIC (Diabetes Mellitus Treatment for Renal Insufficiency Consortium) database. Am J Kidney Dis Off J Natl Kidney Found. 2012;59(1):75–83. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

