Exploring Graph Theory Mechanisms of Fluid Intelligence in the DLPFC: Insights From Resting-State fNIRS Across Various Time Windows
- PMID: 40022279
- PMCID: PMC11870832
- DOI: 10.1002/brb3.70386
Exploring Graph Theory Mechanisms of Fluid Intelligence in the DLPFC: Insights From Resting-State fNIRS Across Various Time Windows
Abstract
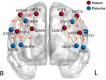
Background: Brain imaging technologies can measure fluid intelligence (gF) levels more directly, objectively, and dynamically, compared to traditional questionnaire scales. To clarify the temporal mechanisms of graph theory in measuring gF, this study investigated the relationship between graph theoretical indicators in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC) and gF levels under various time windows.
Methods: Using 30-min resting-state fNIRS (rs-fNIRS) data and Raven's Advanced Progressive Matrices from 116 healthy participants, the relationship between individual gF levels and DLPFC brain signals was analyzed using average degree (AD) and global efficiency (Eglob).
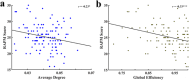
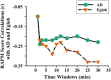
Results: AD and Eglob in the resting-state DLPFC were significantly negatively correlated with the RAPM score. Considering the effectiveness and efficiency of gF measurement, a 2-min data collection might suffice, while for Eglob, more than 15-min collection was more effective.
Conclusion: These findings help clarify brain indicators and demonstrate the effectiveness of rs-fNIRS in intelligence measurement, providing a theoretical and practical basis for portable and objective gF assessment .
Keywords: DLPFC; fluid intelligence; resting‐state fNIRS; time‐windowed graph theory.
© 2025 The Author(s). Brain and Behavior published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Andellini, M. , Cannatà V., Gazzellini S., Bernardi B., and Napolitano A.. 2015. “Test‐Retest Reliability of Graph Metrics of Resting State MRI Functional Brain Networks: A Review.” Journal of Neuroscience Methods 253: 183–192. - PubMed
-
- Cattell, R. B. 1971. Abilities: Their Structure, Growth, and Action. Houghton Mifflin.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- the National Natural Science Foundation Project of China
- Humanity and Social Science Research Project of Jiangxi Educational Committee
- Technology Planning Project of Health Commission of Jiangxi Province
- Graduate Innovation Special Fund of Jiangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine Science and Technology Innovation Team Development Program
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

