Genomically defined hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae contributed to early-onset increased mortality
- PMID: 40025046
- PMCID: PMC11873152
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-57379-4
Genomically defined hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae contributed to early-onset increased mortality
Abstract
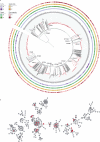
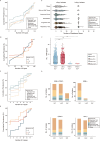
The presence of all five of the virulence-associated genes iucA, iroB, peg-344, rmpA, and rmpA2 is presently the most accurate genomic means for predicting hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae (hvKp-p). With this longitudinal cohort study, we firstly provide novel insights into the clinical and genomic characteristics of hvKp-p in high-risk regions. Through propensity score matching, we show that hvKp-p is less likely to acquire antimicrobial resistance but develops more severe disease and result in increased mortality. HvKp-p are predominantly isolated from hospital settings and caused pneumonia in majority of the cases. ST23 and KL1 are the most common types in the hvKp-p cohort. Community-acquired and healthcare-associated infections are also identified as independent risk factors for hvKp-p. This genomic definition, albeit imperfect, offers a practical and efficient alternative to murine models, allowing for early identification and timely intervention in clinical settings.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Liu, C. et al. An increased prevalence of carbapenem-resistant hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae associated with the COVID-19 pandemic. Drug Resist. Updat.77, 101124 (2024). - PubMed
-
- Wang, Q. et al. Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae: data from a longitudinal large-scale CRE study in China (2012-2016). Clin. Infect. Dis.67, S196–S205 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Liu, C., Guo, J., Lu, M., Shen, N. & Du, P. Dissemination of the mobilised RND efflux pump gene cluster tmexCD-toprJ among Klebsiella pneumoniae. The Lancet. Microbe4, e135 (2023). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- I01 BX004677/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- R21 AI141826/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- NIH 1R21AI141826-01A1/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)
- No. 82200012/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

