Canonical and non-canonical functions of the non-coding RNA component (TERC) of telomerase complex
- PMID: 40025596
- PMCID: PMC11871756
- DOI: 10.1186/s13578-025-01367-0
Canonical and non-canonical functions of the non-coding RNA component (TERC) of telomerase complex
Abstract
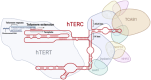
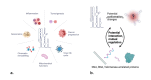
The telomerase complex consists of a protein component (TERT), which has reverse transcriptase activity, and an RNA component (TERC), which serves as a template for telomere synthesis. Evidence is rapidly accumulating regarding the non-canonical functions of these components in both normal or diseased cells. An oligonucleotide-based drug, the first telomerase inhibitor, secured FDA approval in June 2024. We recently summarized the non-canonical functions of TERT in viral infections and cancer. In this review, we expand on these non-canonical functions of TERC beyond telomere maintenance. Specifically, we explore TERC's roles in cellular aging and senescence, immune regulation, genetic diseases, human cancer, as well as involvement in viral infections and host interactions. Finally, we discuss a transcription product of telomere repeats, TERRA, and explore strategies for targeting TERC as a therapeutic approach.
Keywords: Non-canonical functions; Non-coding RNAs; TERC; TERT; Telomerase; Telomeres.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors have nothing to report.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Long non-coding RNAs at work on telomeres: Functions and implications in cancer therapy.Cancer Lett. 2021 Apr 1;502:120-132. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2020.12.036. Epub 2021 Jan 13. Cancer Lett. 2021. PMID: 33450357
-
Telomere-independent functions of telomerase in nuclei, cytoplasm, and mitochondria.Front Oncol. 2012 Sep 28;2:133. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2012.00133. eCollection 2012. Front Oncol. 2012. PMID: 23061047 Free PMC article.
-
Telomerase reverse transcriptase in the regulation of gene expression.BMB Rep. 2014 Jan;47(1):8-14. doi: 10.5483/bmbrep.2014.47.1.284. BMB Rep. 2014. PMID: 24388106 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dissecting the non-canonical functions of telomerase.Cytogenet Genome Res. 2008;122(3-4):273-80. doi: 10.1159/000167813. Epub 2009 Jan 30. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2008. PMID: 19188696 Review.
-
Current Insights to Regulation and Role of Telomerase in Human Diseases.Antioxidants (Basel). 2017 Feb 28;6(1):17. doi: 10.3390/antiox6010017. Antioxidants (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28264499 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nakamura TM, Morin GB, Chapman KB, Weinrich SL, Andrews WH, Lingner J, Harley CB, Cech TR. Telomerase catalytic subunit homologs from fission yeast and human. Science. 1997;277:955–9. - PubMed
-
- Autexier C, Lue NF. The structure and function of telomerase reverse transcriptase. Annu Rev Biochem. 2006;75:493–517. - PubMed
-
- Greider CW, Blackburn EH. Identification of a specific telomere terminal transferase activity in Tetrahymena extracts. Cell. 1985;43:405–13. - PubMed
-
- Morin GB. The human telomere terminal transferase enzyme is a ribonucleoprotein that synthesizes TTAGGG repeats. Cell. 1989;59:521–9. - PubMed
-
- Harrington L, McPhail T, Mar V, Zhou W, Oulton R, Bass MB, Arruda I, Robinson MO. A mammalian telomerase-associated protein. Science. 1997;275:973–7. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
- R01 CA276474/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA222148/Division of Cancer Epidemiology and Genetics, National Cancer Institute
- U01 CA278927/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R33CA258016/Division of Cancer Epidemiology and Genetics, National Cancer Institute
- U01CA278927/Division of Cancer Prevention, National Cancer Institute
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

