Taurine promotes glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion in enteroendocrine L cells
- PMID: 40026256
- PMCID: PMC12147438
- DOI: 10.1002/1873-3468.70014
Taurine promotes glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion in enteroendocrine L cells
Abstract
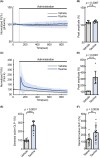
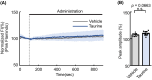
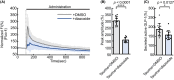
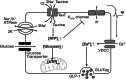
Taurine, an amino-sulfonic acid mainly sourced from food, suppresses blood glucose by stimulating insulin secretion from pancreatic β-cells. However, its relationship with glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) secretion from enteroendocrine L cells is unclear. This study aimed to determine the role of taurine in GLP-1 secretion from L cells. Taurine administration promoted GLP-1 secretion in enteroendocrine L cell line GLUTag cells and increased plasma GLP-1 in mice. Taurine uptake via the taurine transporter increased cytosolic ATP levels, resulting in higher intracellular Ca2+ concentrations and enhanced GLP-1 secretion through ATP-sensitive K+ channel closure. These findings may help identify new therapeutic targets for obesity and diet-related disease prevention.
Keywords: GLUTag; glucagon‐like peptide‐1; live‐cell imaging; taurine; taurine transporter.
© 2025 The Author(s). FEBS Letters published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Figures


References
-
- Furness JB, Rivera LR, Cho H‐J, Bravo DM and Callaghan B (2013) The gut as a sensory organ. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 10, 729–740. - PubMed
-
- Baggio LL and Drucker DJ (2007) Biology of incretins: GLP‐1 and GIP. Gastroenterology 132, 2131–2157. - PubMed
-
- Campbell JE and Drucker DJ (2013) Pharmacology, physiology, and mechanisms of incretin hormone action. Cell Metab 17, 819–837. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

