Construction Site Noise Exposure Assessment Using Binaural Measurements and Analysis
- PMID: 40026880
- PMCID: PMC11870672
- DOI: 10.3390/safety10040092
Construction Site Noise Exposure Assessment Using Binaural Measurements and Analysis
Abstract
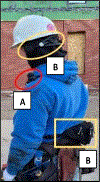
Acoustic measures of construction site noise are important for hearing loss prevention and safety. This work examines noise exposure assessment using binaural measurements to pave the way for more accurate noise characterization and hearing loss prevention in loud workplaces. Recordings were made over three days on a construction site, and noise exposure was estimated using state-of-the-art methods (a shoulder-worn dosimeter) and binaural measurements (microphones at each ear). For the binaural assessment, noise exposure was quantified at each ear to identify the higher- and lower-exposure ears, and the assessment incorporated kurtosis, a statistical measure that quantifies impulsiveness of the noise. The impulsiveness of the noise of four construction tools was also assessed. For this set of measurements, traditional hearing loss risk assessment consistently underestimated the noise exposure relative to binaural assessment. Moreover, the binaural measurement method exposed multiple cases of asymmetric noise exposure that are not detectable using the traditional method. Overall, there are clear benefits to assessing risk using binaural measurements and more detailed analysis methods.
Keywords: binaural measurement and analysis; kurtosis; noise exposure assessment; sound impulsiveness.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: Author Haitham Sarsam was employed by the company O’Brien Construction Company, Inc. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Ringen K; Dement JM; Quinn P; Cloeren M; Chen A; Cranford K; Haas S Hearing impairment and tinnitus among older construction workers employed at DOE facilities. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2022, 65, 644–651. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
