Noninvasive Quantification of Hepatic Steatosis Using Ultrasound-Derived Fat Fraction (CHESS2303): A Prospective Multicenter Study
- PMID: 40027150
- PMCID: PMC11868440
- DOI: 10.1002/mco2.70123
Noninvasive Quantification of Hepatic Steatosis Using Ultrasound-Derived Fat Fraction (CHESS2303): A Prospective Multicenter Study
Abstract
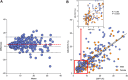
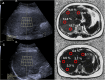
Ultrasound-derived fat fraction (UDFF) is designed to assess the hepatic fat content quantitatively. A multicenter study that verifies the diagnostic performance of UDFF for detecting hepatic steatosis has not yet been reported. This study aimed to evaluate the performance of UDFF for diagnosing and grading hepatic steatosis. Participants referred for assessment of hepatic steatosis were prospectively recruited from eight hospitals. All participants underwent UDFF and magnetic resonance imaging proton density fat fraction (MRI-PDFF) examinations. MRI-PDFF was used as the reference for diagnosing hepatic steatosis. From January 2023 to July 2023, a total of 300 participants were included. The median body mass index was 25.4 kg/m2 (interquartile range: 22.7-28.1). UDFF values were positively correlated with MRI-PDFF (R = 0.80, p < 0.001). Using MRI-PDFF ≥ 5%, ≥ 15%, and ≥ 25% as the reference standard for detecting mild, moderate, and severe hepatic steatosis, the best cutoff values of UDFF were 7.6% (area under the receiver operating characteristic curves [AUC] = 0.90), 15.9% (AUC = 0.90), and 22.3% (AUC = 0.91), respectively. Thus, UDFF has excellent diagnostic performance in detecting and grading hepatic steatosis.
Keywords: hepatic steatosis; magnetic resonance imaging proton density fat fraction (MRI‐PDFF); noninvasive; quantification; ultrasound‐derived fat fraction (UDFF).
© 2025 The Author(s). MedComm published by Sichuan International Medical Exchange & Promotion Association (SCIMEA) and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declared no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Rinella M. E., Lazarus J. V., Ratziu V., et al., “A Multisociety Delphi Consensus Statement on New Fatty Liver Disease Nomenclature,” Journal of Hepatology 79, no. 6 (2023): 1542–1556. - PubMed
-
- Wong V. W., Ekstedt M., Wong G. L., and Hagström H., “Changing Epidemiology, Global Trends and Implications for Outcomes of NAFLD,” Journal of Hepatology 79, no. 3 (2023): 842–852. - PubMed
-
- Pitisuttithum P. and Treeprasertsuk S., “Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Among Older Adults,” Portal Hypertension & Cirrhosis 1, no. 3 (2022): 184–191.
-
- Miao L., Targher G., Byrne C. D., Valenti L., Qi X., and Zheng M.‐H., “Portal Hypertension in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Challenges and Perspectives,” Portal Hypertension & Cirrhosis 1, no. 1 (2022): 57–65.
-
- Guo H., Ni H., Xue J., et al., “Global Scientific Trends on Portal Hypertension and Cirrhosis in the 21st Century: A Bibliometric and Visualized Analysis,” Portal Hypertension & Cirrhosis 2, no. 1 (2023): 46–48.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
