Post-transplant cyclophosphamide-induced cardiotoxicity: A comprehensive review
- PMID: 40027370
- PMCID: PMC11866776
- DOI: 10.34172/jcvtr.33230
Post-transplant cyclophosphamide-induced cardiotoxicity: A comprehensive review
Abstract
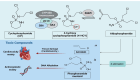
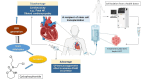
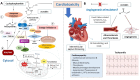
Cyclophosphamide-induced cardiotoxicity, associated with its toxic metabolite acrolein, is a significant concern and unresolved issue, especially when cyclophosphamide is administrated in high doses. However, cardiotoxicity following low-dose cyclophosphamide has been also documented, especially in post-hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (post-HSCT) settings. Despite the involvement of multiple signaling pathways in cyclophosphamide-induced cardiomyopathy, the exact underlying mechanisms remain to be fully elucidated. This review outlines the current challenges of cyclophosphamide therapy in HSCT recipients. In addition, the promising therapeutic approaches by targeting acrolein's anti-angiogenic effect were thoroughly discussed to better manage post-HSCT cyclophosphamide-induced cardiotoxicity.
Keywords: Acrolein; Angiogenesis; Cardiotoxicity; Cyclophosphamide; Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared that they have no conflict of interest regarding this work.
References
-
- Zhang L, Zhou J, Hu L, Han X, Zou X, Chen Q, et al. In situ formed fibrin scaffold with cyclophosphamide to synergize with immune checkpoint blockade for inhibition of cancer recurrence after surgery. Adv Funct Mater. 2020;30(7):1906922. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201906922. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources