Selective dual-mode detection of reactive oxygen species and metal ions by chemodosimetric vs. chelation pathways: fluorescence 'turn-on' with OCl- and Zn2+/Mn2+, employing theoretical, practical, and bioimaging applications
- PMID: 40027582
- PMCID: PMC11869208
- DOI: 10.1039/d4ra08191a
Selective dual-mode detection of reactive oxygen species and metal ions by chemodosimetric vs. chelation pathways: fluorescence 'turn-on' with OCl- and Zn2+/Mn2+, employing theoretical, practical, and bioimaging applications
Abstract
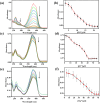
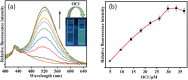
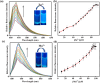
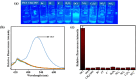
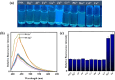
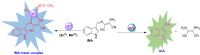
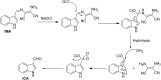
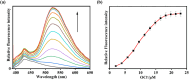
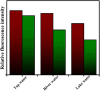
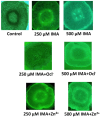
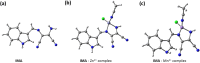
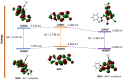
An indole-coupled diaminomaleonitrile-based fluorescent chemosensor IMA has been designed and developed for the selective detection of ROS (OCl-) and metal ions Zn2+ and Mn2+ via chemodosimetric and chelation pathways respectively. The selective sensing of OCl- is induced by a method of oxidatively cleaving of the imine bond of IMA, forming free indole aldehyde, which results in a 21-fold enhancement of fluorescence at 521 nm, with a detection limit of 2.8 µM. On the other hand, the selective binding of IMA with Zn2+ and Mn2+ results in chelation-induced enhanced fluorescence (CHEF) and increased intermolecular charge transfer (ICT), leading to a 4-fold and 3-fold fluorescence enhancement at 432 nm and 435 nm, with the detection limits of 12.71 µM and 17.34 µM, respectively. UV-vis spectroscopy, fluorescence, DFT study, mass spectra, 1H-NMR analysis, and Job's plot analysis have been used to validate the sensing mechanism of IMA with OCl-, Zn2+, and Mn2+. For practical applications, the binding of IMA with OCl- has been utilized in the detection of commercial samples like bleaching powder and water analysis. Bio-imaging studies were conducted with IMA in the presence of OCl- and Zn2+ using green gram seeds in a physiological medium.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
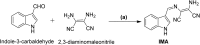
References
-
- Wu J. Liu W. Ge J. Zhang H. Wang P. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011;40:3483–3495. - PubMed
-
- Wu S.-P. Du K.-J. Sung Y.-M. Dalton Trans. 2010;39:4363–4368. - PubMed
-
- Jiang Y. Zheng G. Duan Q. Yang L. Zhang J. Zhang H. He J. Sun H. Ho D. Chem. Commun. 2018;54:7967–7970. - PubMed
-
- Ji R. Qin K. Liu A. Zhu Y. Ge Y. Tetrahedron Lett. 2018;59:2372–2375.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

