This is a preprint.
Generation of antigen-specific paired chain antibody sequences using large language models
- PMID: 40027781
- PMCID: PMC11870394
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.12.20.629482
Generation of antigen-specific paired chain antibody sequences using large language models
Update in
-
Generation of antigen-specific paired-chain antibodies using large language models.Cell. 2025 Nov 4:S0092-8674(25)01135-3. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2025.10.006. Online ahead of print. Cell. 2025. PMID: 41192421
Abstract
The traditional process of antibody discovery is limited by inefficiency, high costs, and low success rates. Recent approaches employing artificial intelligence (AI) have been developed to optimize existing antibodies and generate antibody sequences in a target-agnostic manner. In this work, we present MAGE (Monoclonal Antibody GEnerator), a sequence-based Protein Language Model (PLM) fine-tuned for the task of generating paired human variable heavy and light chain antibody sequences against targets of interest. We show that MAGE can generate novel and diverse antibody sequences with experimentally validated binding specificity against SARS-CoV-2, an emerging avian influenza H5N1, and respiratory syncytial virus A (RSV-A). MAGE represents a first-in-class model capable of designing human antibodies against multiple targets with no starting template.
Conflict of interest statement
I.S.G. is a cofounder of AbSeek Bio. P.T.W and I.S.G. are listed as inventors on patents filed describing the pipeline presented here for the fine-tuning of LLMs for antigen-specific antibody generation. The Georgiev laboratory has received unrelated funding from Takeda and Merck. Dr. Chu has consulted for Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation and Ellume, and has served on advisory boards for Vir, Merck and Abbvie; she has received research funding from Gates Ventures, and support and reagents from Ellume and Cepheid outside of the submitted work.
Figures



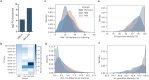


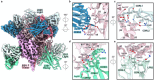
References
-
- Shanehsazzadeh A. et al. , In vitrovalidated antibody design against multiple therapeutic antigens using generative inverse folding. bioRxiv, 2023.2012.2008.570889 (2023).
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
