Enhanced HDR-mediated correction of heterozygous COL7A1 mutations for recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa
- PMID: 40027886
- PMCID: PMC11872078
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omtn.2025.102472
Enhanced HDR-mediated correction of heterozygous COL7A1 mutations for recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa
Abstract
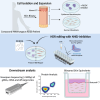
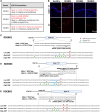
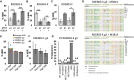
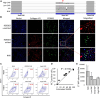
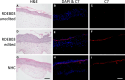
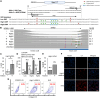
Gene editing facilitated by homology-directed repair (HDR) holds great potential for treating monogenetic disorders such as recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (RDEB). However, low efficiency and variability between loci must be overcome for its widespread adoption into personalized therapies. To address these challenges, we developed a highly efficient and versatile gene editing strategy for RDEB that incorporates the small molecule inhibitor M3814 to enhance HDR. We focused on three RDEB causative COL7A1 mutations not previously targeted by existing gene therapies. Editing was achieved using Cas9-nuclease ribonucleoproteins with short single-stranded DNA donor templates, and outcomes were assessed with an Oxford Nanopore Technology sequencing analysis pipeline. We demonstrate precise genomic HDR rates of up to 75% of alleles in primary RDEB keratinocytes and 32% in fibroblasts. This approach restored collagen VII expression in up to 80% of keratinocytes within a bulk-edited population and resulted in correct collagen VII deposition in a 3D skin model. Additionally, at one locus we show that a dual Cas9-nickase strategy is less effective than Cas9-nuclease and prone to large on-target deletions. Our results demonstrate a significant advancement in the efficiency and consistency of HDR editing, potentially paving the way for more effective personalized gene therapies.
Keywords: CRISPR-Cas9; MT: RNA/DNA Editing; Oxford Nanopore Technology sequencing; dual-nickase; epidermolysis bullosa; gene therapy; homology-directed repair; skin engineering.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

