Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway: an attractive potential therapeutic target in osteosarcoma
- PMID: 40028002
- PMCID: PMC11867957
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1456959
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway: an attractive potential therapeutic target in osteosarcoma
Abstract
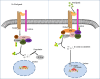
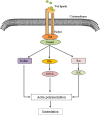
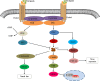
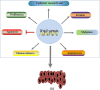
Osteosarcoma (OS) is the most common bone malignancy in children and adolescents, and although current neoadjuvant chemotherapy has shown efficacy against OS, the long-term survival rate for patients with OS remains low, highlighting the need to find more effective treatments. In cancer cells, abnormal activation of signaling pathways can widely affect cell activity from growth and proliferation to apoptosis, invasion and metastasis. Wnt/β-catenin is a complex and unique signaling pathway that is considered to be one of the most important carcinogenic pathways in human cancer. Research have confirmed that the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway is an important driving factor for the occurrence and development of osteosarcoma, and abnormal activation of this pathway can promote the pathological processes of cell proliferation, invasion, migration, tumor angiogenesis and chemical resistance of osteosarcoma. However, inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway can effectively inhibit or reverse the above pathological processes. Therefore, manipulating the expression or function of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway may be a potential targeted pathway for the treatment of OS. In this review, we describe the characteristics of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and summarize the role and mechanism of this pathway in OS. This paper discusses the therapeutic significance of inhibiting or targeting Wnt/β-catenin pathway in OS and the shortcomings of current studies on this pathway in OS and the problems to be solved. This review helps us to understand the role of Wnt/β-catenin on OS, and provides a theoretical basis and new ideas for targeting Wnt/β-catenin pathway as a therapeutic target for OS.
Keywords: Wnt/β-catenin; chemotherapy; mechanism; osteosarcoma (OS); targeted therapy.
Copyright © 2025 Ding and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Down-regulation of microRNA-31-5p inhibits proliferation and invasion of osteosarcoma cells through Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway by enhancing AXIN1.Exp Mol Pathol. 2019 Jun;108:32-41. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2019.03.001. Epub 2019 Mar 4. Exp Mol Pathol. 2019. PMID: 30844369
-
Ziyuglycoside II, a triterpene glycoside compound in Sanguisorbae officinalis l. extract, suppresses metastasis in osteosarcoma via CBX4-mediated Wnt/β-catenin signal pathway.Phytomedicine. 2024 Sep;132:155716. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155716. Epub 2024 May 9. Phytomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38924929
-
Convallatoxin suppresses osteosarcoma cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and enhances osteogenic differentiation by downregulating parathyroid hormone receptor 1 (PTHR1) expression and inactivating Wnt/β-catenin pathway.Bioengineered. 2022 May;13(5):13280-13292. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2080363. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35635031 Free PMC article.
-
The canonical Wnt-beta-catenin pathway in development and chemotherapy of osteosarcoma.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2013 Jun 1;18(4):1384-91. doi: 10.2741/4187. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2013. PMID: 23747891 Review.
-
Wnt signaling in osteosarcoma.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014;804:33-45. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-04843-7_2. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014. PMID: 24924167 Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

