A chionodracine-derived peptide, KHS-Cnd, as an anti-virulence agent against multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii clinical strains
- PMID: 40028178
- PMCID: PMC11868114
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1526246
A chionodracine-derived peptide, KHS-Cnd, as an anti-virulence agent against multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii clinical strains
Abstract
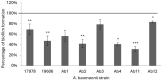
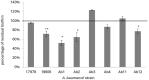
About 71% of healthcare-associated infections are due to antibiotic-resistant bacteria, such as carbapenem-resistant A. baumannii, classified by World Health Organization into a critical priority group of pathogens. The antimicrobial resistance profile of A. baumannii relies on its ability to produce several virulence factors, including biofilm formation. Its ability to adhere and persist on surfaces as biofilm has contributed to its pathogenicity and drug resistance. In this study, the ability of an antimicrobial peptide (a chionodracine-derived peptide named KHS-Cnd) to inhibit or reduce biofilm formation was investigated as an example of a potential strategy to counteract infections caused by biofilm-forming pathogens. To this aim, the antimicrobial profiles were first analyzed in selected A. baumannii strains, two reference and six clinical strains, all biofilm-forming with different capability, regardless of whether they are drug resistant or sensitive. Successively, we investigated the bactericidal activity of the peptide that showed MIC values ranging from 5 to 10 µM and a significative antibiofilm activity on all tested strains at sub-inhibitory concentrations. In fact, KHS-Cnd can hinder biofilm A. baumannii strains formation with an inhibition percentage ranging between 65% and 10%. Also a statistically significant reduction of mature biofilm ranging from 20% to 50% was observed in four out of eight tested A. baumannii strains. KHS-Cnd impacts various stages of biofilm formation, including the inhibition of surface-associated and twitching motilities depending on the different strain. In particular, our results showed that only two strains possessed surface-associated motility that was strongly impaired by KHS-Cnd treatment; three clinical strains, instead, showed twitching motility, whose inhibition for two of them was evident after 24 h of incubation with peptide. Moreover, the invasion of pulmonary cells by A. baumannii was significantly impaired with a reduction of about 32% after treatment with 1.25 µM KHS-Cnd. Finally, when the peptide was used together with ceftazidime/avibactam against resistant A. baumannii strains, it was able to reduce the minimal inhibitory concentration of antibiotics needed to inhibit the microorganism growth.
Keywords: Acinetobacter baumannii; antimicrobial peptide; biofilm; surface-associated motility; twitching motility.
Copyright © 2025 Artini, Paris, Imperlini, Buonocore, Vrenna, Papa and Selan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Anti-Virulence Potential of a Chionodracine-Derived Peptide against Multidrug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Clinical Isolates from Cystic Fibrosis Patients.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 4;23(21):13494. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113494. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36362282 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic Inhibitory Effect of Polymyxin B in Combination with Ceftazidime against Robust Biofilm Formed by Acinetobacter baumannii with Genetic Deficiency in AbaI/AbaR Quorum Sensing.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Feb 23;10(1):e0176821. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01768-21. Epub 2022 Feb 23. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35196792 Free PMC article.
-
[Investigation of the virulence factors of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolates].Mikrobiyol Bul. 2014 Jan;48(1):70-81. Mikrobiyol Bul. 2014. PMID: 24506717 Turkish.
-
Quorum-sensing system in Acinetobacter baumannii: a potential target for new drug development.J Appl Microbiol. 2020 Jan;128(1):15-27. doi: 10.1111/jam.14330. Epub 2019 Jun 26. J Appl Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 31102552 Review.
-
Inhibition of Virulence Factors and Biofilm Formation of Acinetobacter Baumannii by Naturally-derived and Synthetic Drugs.Curr Drug Targets. 2021;22(7):734-759. doi: 10.2174/1389450121666201023122355. Curr Drug Targets. 2021. PMID: 33100201 Review.
References
-
- Alexander P. J., Oyama L. B., Olleik H., Godoy Santos F., O’Brien S., Cookson A., et al. . (2024). Microbiome-derived antimicrobial peptides show therapeutic activity against the critically important priority pathogen, Acinetobacter baumannii . NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 10, 92. doi: 10.1038/s41522-024-00560-2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Artini M., Imperlini E., Buonocore F., Relucenti M., Porcelli F., DonFrancesco O., et al. . (2022). Anti-Virulence Potential of a Chionodracine-Derived Peptide against Multidrug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Clinical Isolates from Cystic Fibrosis Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 13494. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113494 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Buonocore F., Picchietti S., Porcelli F., Della Pelle G., Olivieri C., Poerio E., et al. . (2019). Fish-derived antimicrobial peptides: Activity of a chionodracine mutant against bacterial models and human bacterial pathogens. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 96, 9–17. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2019.02.012 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

