Role of contrast-enhanced ultrasound with time-intensity curve analysis about thyroid nodule and parenchyma for differentiating BRAF V600E mutation status
- PMID: 40028210
- PMCID: PMC11869889
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.19006
Role of contrast-enhanced ultrasound with time-intensity curve analysis about thyroid nodule and parenchyma for differentiating BRAF V600E mutation status
Abstract
Background: The BRAF V600E mutation was proven associated with papillary thyroid cancer (PTC) which has more aggressive behavior and could affect the outcome of PTC. The objective of this study was to observe more contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) time-intensity curve (TIC)-based quantitative parameters in nodules and surrounding parenchyma and analyze the association between the TIC-based quantitative parameters and BRAF V600E mutation status in patients with PTC.
Methods: A retrospective analysis of 447 PTC patients was conducted. Prior to thyroidectomy or fine needle aspiration (FNA), all patients had CEUS and had their BRAF V600E mutations examined. Based on their mutation status, the patients were split into two groups. The two groups were compared in terms of sex, age, quantitative CEUS characteristics, pathological findings, vascular invasion, capsular invasion, and cervical lymph node metastases.
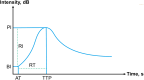
Results: A total of 240 patients were in the mutation negative group and 207 patients were in the BRAF mutation positive group. The BRAF-positive group exhibited significantly higher arrival time (AT) and time to peak enhancement (TTP) of the nodules, among other direct quantitative characteristics. The BRAF-positive mutant nodules showed significantly higher arrival time change and time to peak change compared to the surrounding parenchyma for indirect quantitative metrics.
Conclusion: The time-dependent quantitative parameters of CEUS time intensity curve in nodules and surrounding parenchyma have clinical value in distinguishing BRAF V600E mutation positive nodules from gene mutation negative nodules. Quantitative CEUS characteristics may be beneficial in detecting the BRAF V600E mutation status and informing the subsequent clinical choice.
Keywords: BRAF V600E; Contrast enhanced ultrasound; Papillary thyroid microcarcinoma; Quantitative parameter.
© 2025 Hu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diagnostic Value and Challenges of BRAF V600E Molecular Testing and Thyroid Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology: A Retrospective Study from a Tertiary Institution in Southern Hunan Province, China.Acta Cytol. 2023;67(6):629-638. doi: 10.1159/000534138. Epub 2023 Sep 14. Acta Cytol. 2023. PMID: 37708867
-
Location based BRAF V600E mutation status and dimension patterns of sporadic thyroid nodules: a population-based study.BMC Cancer. 2025 Mar 6;25(1):406. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-13776-y. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40050757 Free PMC article.
-
The Combined Use of Fine-Needle Aspiration (FNA) and BRAF V600E Gene Testing: Can it Increase the Definitive Diagnosis Rate of Nodules Categorized as Bethesda III for Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma?Am Surg. 2024 Dec;90(12):3209-3215. doi: 10.1177/00031348241265143. Epub 2024 Jul 24. Am Surg. 2024. PMID: 39047144
-
Testing for BRAF (V600E) Mutation in Thyroid Nodules with Fine-Needle Aspiration (FNA) Read as Suspicious for Malignancy (Bethesda V, Thy4, TIR4): a Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Endocr Pathol. 2020 Mar;31(1):57-66. doi: 10.1007/s12022-019-09596-z. Endocr Pathol. 2020. PMID: 31811566
-
Accuracy of Radiomics in the Identification of Extrathyroidal Extension and BRAFV600E Mutations in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Acad Radiol. 2025 Mar;32(3):1385-1397. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2024.11.014. Epub 2025 Jan 6. Acad Radiol. 2025. PMID: 39765435
References
-
- Chen L, Chen L, Liu J, Nong L, Zhang H. The association among quantitative contrast-enhanced ultrasonography features, thyroid imaging reporting and data system and BRAF V600E mutation status in patients with papillary thyroid microcarcinoma. Ultrasound Quarterly. 2019;35(3):228–232. doi: 10.1097/RUQ.0000000000000406. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Conzo G, Docimo G, Ruggiero R, Napolitano S, Santini L. Surgical treatment of papillary thyroid carcinoma without lymph nodal involvement. IL Giornale Di Chirurgia. 2012;33(10):339. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials