Sex differences in absolute and relative changes in muscle size following resistance training in healthy adults: a systematic review with Bayesian meta-analysis
- PMID: 40028215
- PMCID: PMC11869894
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.19042
Sex differences in absolute and relative changes in muscle size following resistance training in healthy adults: a systematic review with Bayesian meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Muscle hypertrophy may be influenced by biological differences between males and females. This meta-analysis investigated absolute and relative changes in muscle size following resistance training (RT) between males and females and whether measures of muscle size, body region assessed, muscle fibre type, and RT experience moderate the results.
Methods: Studies were included if male and female participants were healthy (18-45 years old) adults that completed the same RT intervention, and a measure of pre- to post-intervention changes in muscle size was included. Out of 2,720 screened studies, 29 studies were included in the statistical analysis. Bayesian methods were used to estimate a standardised mean difference (SMD), log response ratio (lnRR) with exponentiated percentage change (Exp. % Change of lnRR), and probability of direction (pd) for each outcome.
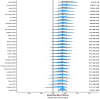
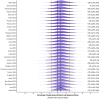
Results: Absolute increases in muscle size slightly favoured males compared to females (SMD = 0.19 (95% HDI: 0.11 to 0.28); pd = 100%), however, relative increases in muscle size were similar between sexes (Exp. % Change of lnRR = 0.69% (95% HDI: -1.50% to 2.88%)). Outcomes were minimally influenced by the measure of muscle size and not influenced by RT experience of participants. Absolute hypertrophy of upper-body but not lower-body regions was favoured in males. Type I muscle fibre hypertrophy slightly favoured males, but Type II muscle fibre hypertrophy was similar between sexes.
Conclusion: Our findings strengthen the understanding that females have a similar potential to induce muscle hypertrophy as males (particularly when considering relative increases in muscle size from baseline) and findings of our secondary analyses should inform future research that investigates sex differences in highly trained participants and muscle fibre type-specific hypertrophy.
Keywords: Gender difference; Muscle hypertrophy; Muscle size; Resistance training; Sex difference.
©2025 Refalo et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Lee Hamilton, Jackson Fyfe, and Iain Gallagher declare that they have no conflicts of interest or competing interests. Martin Refalo, Greg Nuckols, and Andrew Galpin are all coaches and writers in the fitness industry. Greg Nuckols is the founder of Stronger by Science LLC. No known companies will benefit from the results of the present study.
Figures
References
-
- Abou Sawan S, Hodson N, Babits P, Malowany JM, Kumbhare D, Moore DR. Satellite cell and myonuclear accretion is related to training-induced skeletal muscle fiber hypertrophy in young males and females. Journal of Applied Physiology. 2021;131:871–880. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00424.2021. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Abou Sawan S, Hodson N, Malowany JM, West DWD, Tinline-Goodfellow C, Brook MS, Smith K, Atherton PJ, Kumbhare D, Moore DR. Trained integrated postexercise myofibrillar protein synthesis rates correlate with hypertrophy in young males and females. Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise. 2022;54:953–964. doi: 10.1249/MSS.0000000000002878. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

