Review of mechanisms and frontier applications in IL-17A-induced hypertension
- PMID: 40028265
- PMCID: PMC11868716
- DOI: 10.1515/med-2025-1159
Review of mechanisms and frontier applications in IL-17A-induced hypertension
Abstract
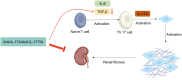
Background: The immune system is closely related to hypertension. Hypertension is an immune disorder to a certain extent, and inflammation is the basis of abnormally elevated blood pressure (BP). The accumulation of T cells and their cytokines can increase BP and end organ damage. T cells are activated by antigen-presenting cells of the innate immune system or by the influence of a high-sodium diet, the self-environment, or the gut microbiota. These cells produce inflammatory factors and cytokines, such as interleukin-17A (IL-17A) in T helper 17 cells, causing vascular inflammation, hypertension, and target organ damage.
Methods: In this article, we provide an insightful review of the research progress regarding the role of IL-17A in the pathogenesis of hypertension and its effects on different organs while emphasizing the role of IL-17A and its mediated functions in the kidneys, brain, intestines, and vascular system in the development and progression of hypertension.
Results: At the organ level, IL-17A is involved in the development and progression of hypertension in the kidneys, brain, intestines, and blood vessels, interacting with multiple signal pathway.
Conclusions: These findings have significant implications for developing future immunomodulatory therapies, which may lead to the development of potential treatments for hypertension.
Keywords: T helper 17 cells; hypertension; immunity; inflammation; interleukin 17A.
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors state no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interleukin 17A: Key Player in the Pathogenesis of Hypertension and a Potential Therapeutic Target.Curr Hypertens Rep. 2021 Mar 5;23(3):13. doi: 10.1007/s11906-021-01128-7. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2021. PMID: 33666761 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interleukin-17A: Potential mediator and therapeutic target in hypertension.Nefrologia (Engl Ed). 2021 May-Jun;41(3):244-257. doi: 10.1016/j.nefroe.2021.06.003. Epub 2021 Jul 14. Nefrologia (Engl Ed). 2021. PMID: 36166242 Review.
-
Interleukin-17A: Possible mediator and therapeutic target in hypertension.Nefrologia (Engl Ed). 2021 May-Jun;41(3):244-257. doi: 10.1016/j.nefro.2020.11.009. Epub 2021 Mar 26. Nefrologia (Engl Ed). 2021. PMID: 33775443 Review. English, Spanish.
-
Inhibition of Interleukin 17-A but not Interleukin-17F Signaling Lowers Blood Pressure and Reduces End-organ Inflammation in Angiotensin II-induced Hypertension.JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2016 Dec;1(7):606-616. doi: 10.1016/j.jacbts.2016.07.009. Epub 2016 Nov 16. JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2016. PMID: 28280792 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammation in Salt-Sensitive Hypertension and Renal Damage.Curr Hypertens Rep. 2018 Oct 30;20(12):103. doi: 10.1007/s11906-018-0903-x. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2018. PMID: 30377822 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Association between novel Immune-Inflammatory markers and hypertension patients with coronary heart disease: A Cross-Sectional study based on NHANES (2005-2016).BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2025 Jul 4;25(1):467. doi: 10.1186/s12872-025-04906-2. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2025. PMID: 40615783 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berry SPD-G, Dossou C, Kashif A, Sharifinejad N, Azizi G, Hamedifar H, et al. The role of IL-17 and anti-IL-17 agents in the immunopathogenesis and management of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022;102:108402. - PubMed
-
- Nordlohne J, von Vietinghoff S. Interleukin 17A in atherosclerosis - regulation and pathophysiologic effector function. Cytokine. 2019;122:154089. - PubMed
-
- Liuzzo G, Trotta F, Pedicino D. Interleukin-17 in atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease: the good, the bad, and the unknown. Eur Heart J. 2013;34:556–9. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
