Causes of embryo implantation failure: A systematic review and metaanalysis of procedures to increase embryo implantation potential
- PMID: 40028443
- PMCID: PMC11867936
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1429193
Causes of embryo implantation failure: A systematic review and metaanalysis of procedures to increase embryo implantation potential
Abstract
Introduction: Infertility is characterized by the failure to conceive after 12 months of unprotected sexual intercourse. In assisted reproduction technologies (ARTs), in-vitro fertilization and embryo transfer (IVF-ET) are pivotal, with the quality of embryo quality essential for successful implantation.
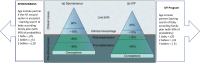
Objective: This systematic review with meta-analysis aimed to explore the prevalence of embryonic factors involved in the implantation process, concentrating on the following research inquiries: 1) the implantation rates of euploid versus untested embryo transfers; 2) the efficiency of transferring good embryos in different age groups; 3) the impact of age on good embryo transfers to gestational carriers; and 4) the transfer of donated gametes/embryos. The goal is to identify critical points in implantation to improve therapies.
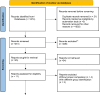
Methods: A comprehensive literature search identified 1474 relevant papers, 11 of which met the inclusion criteria. The information was gathered using a standardized form, and the risk of bias was evaluated. A meta-analysis of subgroups to determine euploid embryo transfer efficiency was conducted to synthesize and explore the results. Furthermore, data extracted from registries document the persistent secondary role of extraembryonic determinants in successful implantation.
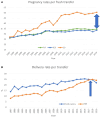
Results: The meta-analysis demonstrated that preimplantation genetic testing for aneuploidy (PGT-A) significantly increased the odds of implantation. Age was found to influence extraembryonic factors, with older women experiencing reduced embryo implantation as gestational carriers. However, the overall incidence of extraembryonic factors was low. This review highlights the need to focus on PGT-A, diagnostic hysteroscopy, and endometrial receptivity for improving implantation rates.
Conclusion: Implantation success in ARTs largely depends on embryo euploidy. While achieving three euploid embryos greatly increases success rates, it is challenging in older women. Extraembryonic factors, although present, have a marginal impact. Subsequent studies ought to concentrate on modulating endometrial responses immunologically and developing algorithms to improve the precision of predicting implantation success; as well as the timing of endometrial receptivity and the occurrence of dormant embryo phenomena also warrants further investigation.
Keywords: assisted reproductive technologies; clinical pregnancy outcomes; euploid embryo transfer; gestational carriers; implantation failure; infertility.
Copyright © 2025 Bulletti, Sciorio, Conforti, De Luca, Bulletti, Palagiano, Berrettini, Scaravelli and Pierson.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
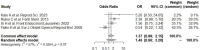
References
-
- Smeenk J, Wyns C, De Geyter C, Kupka M, Bergh C, Saiz Cuevas I, et al. European IVF monitoring consortium (EIM) for the european society of human reproduction and embryology (ESHRE). ART in europe 2019 : results generated from European registries by ESHRE. Hum Reprod. (2023) 38:2321–38. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dead197 - DOI
-
- Calhaz-Jorge C, De Geyter CH, Kupka MS, Wyns C, Mocanu E, Motrenko T, et al. Survey on ART and IUI: legislation, regulation, funding and registries in European countries: The European IVF-monitoring Consortium (EIM) for the European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology (ESHRE). Hum Reprod Open. (2020) 2020:hoz044. doi: 10.1093/hropen/hoz044 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

