MERTK inhibition improves therapeutic efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 40029206
- PMCID: PMC11881874
- DOI: 10.1080/2162402X.2025.2473165
MERTK inhibition improves therapeutic efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
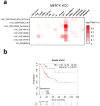
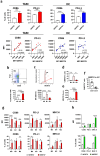
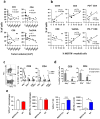
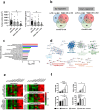
Immunotherapy with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients only achieves response rates of 25%-30%, indicating the necessity of new therapies for non-responder patients. Since myeloid-related suppressive factors are associated with poor responses to ICI in a subgroup of HCC patients, modulation of these targets may improve response rates. Our aim was to characterize the expression of the efferocytosis receptor MERTK in HCC and to analyze its potential as a new therapeutic target. In HCC patients, MERTK was expressed by myeloid cells and was associated with poorer survival. In a murine HCC model with progressive myeloid cell infiltration, MERTK was detected in dendritic cells and macrophages with an activated phenotype, which overexpressed the checkpoint ligand PD-L1. Concomitant expression of PD-1 in tumor T-cells suggested the pertinence of combined PD-1/PD-L1 and MERTK blockade. In vivo experiments in mice showed that inhibition of MERTK improved the therapeutic effect promoted by anti-PD-1 or by ICI combinations currently approved for HCC. This effect was associated with enhanced tumor infiltration and superior activity of antigen presenting cells and effector lymphocytes. Our results indicate that MERTK may behave as a relevant target for immunotherapeutic combinations in those HCC patients with tumors enriched in a myeloid component.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma; MERTK; dendritic cells; immune checkpoint inhibitors; tumor-associated macrophages.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures

References
-
- Zhu AX, Abbas AR, de Galarreta MR, Guan Y, Lu S, Koeppen H, Zhang W, Hsu CH, He AR, Ryoo BY, et al. Molecular correlates of clinical response and resistance to atezolizumab in combination with bevacizumab in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Med. 2022;28(8):1599–1611. doi:10.1038/s41591-022-01868-2. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
