Multivitamins After Myocardial Infarction in Patients With Diabetes: A Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 40029647
- PMCID: PMC11877407
- DOI: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2024.8408
Multivitamins After Myocardial Infarction in Patients With Diabetes: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
Importance: In 2013, the Trial to Assess Chelation Therapy (TACT) reported that in 1708 patients with stable coronary disease and prior myocardial infarction (MI), oral multivitamins and multiminerals (OMVMs), in a factorial design with edetate disodium (EDTA) chelation therapy, did not reduce cardiovascular events relative to placebo OMVMs, but active EDTA combined with active OMVMs was superior to placebo OMVM/placebo EDTA.
Objective: To compare OMVM vs placebo in terms of efficacy for reducing major adverse cardiovascular events in patients with diabetes and prior MI.
Design, setting, and participants: The TACT2 randomized, multicenter double-masked 2 × 2 factorial clinical trial took place across 88 sites in the US and Canada. Participants were 50 years or older, had diabetes, and had an MI 6 weeks ago or more. TACT2 participants were enrolled between September 2016 and December 2020. Data were collected between October 2016 and June 2023.
Interventions: Six caplets daily of a 28 component OMVM or matching OMVM placebo, and 40 weekly infusions of an EDTA-based chelation solution or matching placebo, in a 1:1:1:1 allocation ratio.
Main outcomes and measures: The primary end point was the composite of all-cause mortality, MI, stroke, coronary revascularization, or hospitalization for unstable angina.
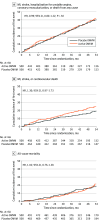
Results: A total of 1000 participants were randomized (500 in the active OMVM group and 500 in the placebo group). The median (IQR) age was 67 (60-72) years, and 730 (73%) were male. Median (IQR) follow-up was 48 (34-58) months. The primary end point occurred in 175 participants (35%) in the active OMVM group and 175 (35%) in the placebo group (hazard ratio [HR], 0.99 [95% CI, 0.80-1.22]; P = .92). The 5-year event rate for the primary end point in the EDTA chelation + active OMVM group was 34.0%; in the EDTA chelation + placebo OMVM group, 35.7%; in the placebo infusion + active OMVM group, 36.0%; and in the placebo infusion + placebo OMVM group, 34.3%. The comparison of the active infusion + active OMVM with the placebo infusion + placebo OMVM was not significant (HR, 0.91 [95% CI, 0.67-1.23]; P = .54). Although nonsignificant, there was a numerically higher event rate of MI, stroke, mortality from cardiovascular causes in the active OMVM compared to placebo OMVM group.
Conclusions and relevance: The results of this randomized clinical trial demonstrated that, for participants with chronic coronary disease, diabetes, and a previous MI, high-dose OMVM alone or in conjunction with EDTA-based chelation did not reduce cardiovascular events.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02733185.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Lamas GA, Boineau R, Goertz C, et al. . EDTA chelation therapy alone and in combination with oral high-dose multivitamins and minerals for coronary disease: the factorial group results of the Trial to Assess Chelation Therapy. Am Heart J. 2014;168(1):37-44.e5. doi:10.1016/j.ahj.2014.02.012 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

