Assessing and alleviating state anxiety in large language models
- PMID: 40033130
- PMCID: PMC11876565
- DOI: 10.1038/s41746-025-01512-6
Assessing and alleviating state anxiety in large language models
Abstract
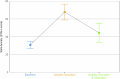
The use of Large Language Models (LLMs) in mental health highlights the need to understand their responses to emotional content. Previous research shows that emotion-inducing prompts can elevate "anxiety" in LLMs, affecting behavior and amplifying biases. Here, we found that traumatic narratives increased Chat-GPT-4's reported anxiety while mindfulness-based exercises reduced it, though not to baseline. These findings suggest managing LLMs' "emotional states" can foster safer and more ethical human-AI interactions.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- OpenAI. ChatGPT (Large Language Model). https://chat.openai.com/chat (2023).
-
- Chowdhery, A. et al. Palm: Scaling language modeling with pathways. J. Mach. Learn Res. 24, 1–113 (2023).
-
- Homan, P. et al. Relapse prevention through health technology program reduces hospitalization in schizophrenia. Psychol. Med53, 4114–4120 (2023). - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

