ZBTB16/PLZF regulates juvenile spermatogonial stem cell development through an extensive transcription factor poising network
- PMID: 40033150
- PMCID: PMC12263333
- DOI: 10.1038/s41594-025-01509-5
ZBTB16/PLZF regulates juvenile spermatogonial stem cell development through an extensive transcription factor poising network
Abstract
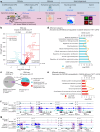
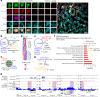
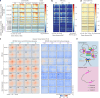
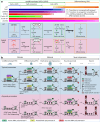
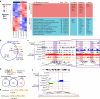
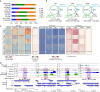
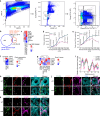
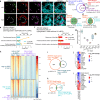
Spermatogonial stem cells balance self-renewal with differentiation and spermatogenesis to ensure continuous sperm production. Here, we identify roles for the transcription factor zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 16 (ZBTB16; also known as promyelocytic leukemia zinc finger (PLZF)) in juvenile mouse undifferentiated spermatogonia (uSPG) in promoting self-renewal and cell-cycle progression to maintain uSPG and transit-amplifying states. Notably, ZBTB16, Spalt-like transcription factor 4 (SALL4) and SRY-box transcription factor 3 (SOX3) colocalize at over 12,000 promoters regulating uSPG and meiosis. These regions largely share broad histone 3 methylation and acetylation (H3K4me3 and H3K27ac), DNA hypomethylation, RNA polymerase II (RNAPol2) and often CCCTC-binding factor (CTCF). Hi-C analyses show robust three-dimensional physical interactions among these cobound promoters, suggesting the existence of a transcription factor and higher-order active chromatin interaction network within uSPG that poises meiotic promoters for subsequent activation. Conversely, these factors do not notably occupy germline-specific promoters driving spermiogenesis, which instead lack promoter-promoter physical interactions and bear DNA hypermethylation, even when active. Overall, ZBTB16 promotes uSPG cell-cycle progression and colocalizes with SALL4, SOX3, CTCF and RNAPol2 to help establish an extensive and interactive chromatin poising network.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: B.R.C. is a cofounder and chair of the scientific advisors of Paterna Biosciences. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures








References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

