Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using neem and turmeric extract and its antimicrobial activity of plant mediated silver nanoparticles
- PMID: 40034373
- PMCID: PMC11875684
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jobcr.2025.02.005
Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using neem and turmeric extract and its antimicrobial activity of plant mediated silver nanoparticles
Abstract
Introduction: The green synthesis of silver nanoparticles has gained attention for being environmentally friendly and cost-effective. This study investigates the synthesis of silver nanoparticles using neem and turmeric extracts, which serve as natural reducing and capping agents, with a focus on characterizing these nanoparticles and assessing their antimicrobial properties against oral pathogens.
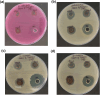
Materials and methods: Neem and turmeric extracts were prepared by heating their powdered forms in distilled water, followed by filtration. The extracts were then mixed with a silver nitrate solution, and the reaction was stirred for 24-48 h. The resulting nanoparticles were characterized using UV-Visible spectroscopy, SEM, EDAX, and XRD analysis. The antimicrobial activity of the nanoparticles was tested against four oral pathogens using the agar well diffusion method.
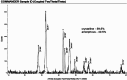
Results: Successful synthesis of silver nanoparticles was confirmed by a color change and characterization analyses. UV-Visible spectroscopy showed a peak at 440 nm, indicating nanoparticle formation. SEM revealed spherical and uniform nanoparticles, while EDAX confirmed the presence of silver. XRD analysis showed the crystalline nature of the nanoparticles, with sizes ranging from 4 nm to 14.81 nm. The nanoparticles exhibited significant antimicrobial activity against Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus mutans, and Lactobacillus species, but were less effective against Candida albicans.
Conclusion: The study demonstrates the effectiveness of neem and turmeric extracts in the green synthesis of silver nanoparticles, which exhibited notable antimicrobial activity. This research underscores the potential of plant-mediated synthesis for developing eco-friendly antimicrobial agents.
Keywords: Antimicrobial agent; Eco-friendly; Green synthesis; Silver nanoparticles.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures





References
-
- Kim S.H., Chung D.R., Song J.-H., et al. Changes in serotype distribution and antimicrobial resistance of Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates from adult patients in Asia: emergence of drug-resistant non-vaccine serotypes. Vaccine. 2020 Aug 27;38(38):6065–6073. - PubMed
-
- Abishad P., Vergis J., Unni V., et al. Green synthesized silver nanoparticles using Lactobacillus acidophilus as an antioxidant, antimicrobial, and antibiofilm agent against multi-drug resistant enteroaggregative Escherichia coli. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2022 Oct;14(5):904–914. - PubMed
-
- Aziz Mousavi SMA., Mirhosseini S.A., Rastegar Shariat Panahi M., Mahmoodzadeh Hosseini H. Characterization of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles using Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG and its in vitro assessment against colorectal cancer cells. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2020 Jun;12(2):740–746. - PubMed
-
- Alzain H., Hussein K., Jabr I., Alsubaie A. Biodegradation of synthetic PVP biofilms using natural materials and nanoparticles. Green Process Synth [Internet] 2023 Jan 23;12(1)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

